An ABCC8 Nonsense Mutation Causing Neonatal Diabetes Through Altered Transcript Expression
- PMID: 28663158
- PMCID: PMC5596808
- DOI: 10.4274/jcrpe.4624
An ABCC8 Nonsense Mutation Causing Neonatal Diabetes Through Altered Transcript Expression
Abstract
The pancreatic ATP-sensitive K+ (K-ATP) channel is a key regulator of insulin secretion. Gain-of-function mutations in the genes encoding the Kir6.2 (KCNJ11) and SUR1 (ABCC8) subunits of the channel cause neonatal diabetes, whilst loss-of-function mutations in these genes result in congenital hyperinsulinism. We report two patients with neonatal diabetes in whom we unexpectedly identified recessively inherited loss-of-function mutations. The aim of this study was to investigate how a homozygous nonsense mutation in ABCC8 could result in neonatal diabetes. The ABCC8 p.Glu747* was identified in two unrelated Vietnamese patients. This mutation is located within the in-frame exon 17 and RNA studies confirmed (a) the absence of full length SUR1 mRNA and (b) the presence of the alternatively spliced transcript lacking exon 17. Successful transfer of both patients to sulphonylurea treatment suggests that the altered transcript expression enhances the sensitivity of the K-ATP channel to Mg-ADP/ATP. This is the first report of an ABCC8 nonsense mutation causing a gain-of-channel function and these findings extend the spectrum of K-ATP channel mutations observed in patients with neonatal diabetes.
Keywords: Neonatal diabetes; nonsense mutation splicing..
Figures
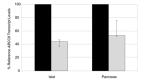
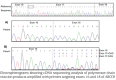
References
-
- Flanagan SE, Clauin S, Bellanne-Chantelot C, Lonlay P, de, Harries LW, Gloyn AL, Ellard S. Update of mutations in the genes encoding the pancreatic beta-cell K(ATP) channel subunits Kir6.2 (KCNJ11) and sulfonylurea receptor 1 (ABCC8) in diabetes mellitus and hyperinsulinism. Human mutation. 2009;30:170–180. - PubMed
-
- Taschenberger G, Mougey A, Shen S, Lester LB, LaFranchi S, Shyng SL. Identification of a familial hyperinsulinism-causing mutation in the sulfonylurea receptor 1 that prevents normal trafficking and function of KATP channels. J Biol Chem. 2002;277:17139–17146. - PubMed
-
- Huopio H, Shyng SL, Otonkoski T, Nichols CG. K(ATP) channels and insulin secretion disorders. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2002;283:207–216. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
