The Histone Methyltransferase MLL1 Directs Macrophage-Mediated Inflammation in Wound Healing and Is Altered in a Murine Model of Obesity and Type 2 Diabetes
- PMID: 28663191
- PMCID: PMC5566299
- DOI: 10.2337/db17-0194
The Histone Methyltransferase MLL1 Directs Macrophage-Mediated Inflammation in Wound Healing and Is Altered in a Murine Model of Obesity and Type 2 Diabetes
Abstract
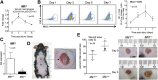
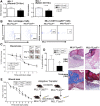
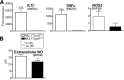
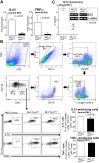
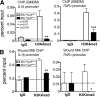
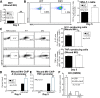
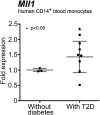
Macrophages are critical for the initiation and resolution of the inflammatory phase of wound repair. In diabetes, macrophages display a prolonged inflammatory phenotype in late wound healing. Mixed-lineage leukemia-1 (MLL1) has been shown to direct gene expression by regulating nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB)-mediated inflammatory gene transcription. Thus, we hypothesized that MLL1 influences macrophage-mediated inflammation in wound repair. We used a myeloid-specific Mll1 knockout (Mll1f/fLyz2Cre+ ) to determine the function of MLL1 in wound healing. Mll1f/fLyz2Cre+ mice display delayed wound healing and decreased wound macrophage inflammatory cytokine production compared with control animals. Furthermore, wound macrophages from Mll1f/fLyz2Cre+ mice demonstrated decreased histone H3 lysine 4 trimethylation (H3K4me3) (activation mark) at NF-κB binding sites on inflammatory gene promoters. Of note, early wound macrophages from prediabetic mice displayed similarly decreased MLL1, H3K4me3 at inflammatory gene promoters, and inflammatory cytokines compared with controls. Late wound macrophages from prediabetic mice demonstrated an increase in MLL1, H3K4me3 at inflammatory gene promoters, and inflammatory cytokines. Prediabetic macrophages treated with an MLL1 inhibitor demonstrated reduced inflammation. Finally, monocytes from patients with type 2 diabetes had increased Mll1 compared with control subjects without diabetes. These results define an important role for MLL1 in regulating macrophage-mediated inflammation in wound repair and identify a potential target for the treatment of chronic inflammation in diabetic wounds.
© 2017 by the American Diabetes Association.
Figures

References
-
- Faglia E, Favales F, Morabito A. New ulceration, new major amputation, and survival rates in diabetic subjects hospitalized for foot ulceration from 1990 to 1993: a 6.5-year follow-up. Diabetes Care 2001;24:78–83 - PubMed
-
- Izumi Y, Satterfield K, Lee S, Harkless LB, Lavery LA. Mortality of first-time amputees in diabetics: a 10-year observation. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 2009;83:126–131 - PubMed
-
- Mirza R, Koh TJ. Dysregulation of monocyte/macrophage phenotype in wounds of diabetic mice. Cytokine 2011;56:256–264 - PubMed
-
- Falanga V. Wound healing and its impairment in the diabetic foot. Lancet 2005;366:1736–1743 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

