Testicular vs adrenal sources of hydroxy-androgens in prostate cancer
- PMID: 28663228
- PMCID: PMC5593253
- DOI: 10.1530/ERC-17-0107
Testicular vs adrenal sources of hydroxy-androgens in prostate cancer
Abstract
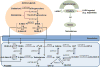
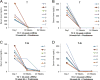
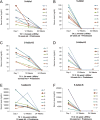
Neoadjuvant androgen deprivation therapy (NADT) is one strategy for the treatment of early-stage prostate cancer; however, the long-term outcomes of NADT with radical prostatectomy including biochemical failure-free survival are not promising. One proposed mechanism is incomplete androgen ablation. In this study, we aimed to evaluate the efficiency of serum hydroxy-androgen suppression in patients with localized high-risk prostate cancer under NADT (leuprolide acetate plus abiraterone acetate and prednisone) and interrogate the primary sources of circulating hydroxy-androgens using our recently described stable isotope dilution liquid chromatography mass spectrometric method. For the first time, three androgen diols including 5-androstene-3β,17β-diol (5-adiol), 5α-androstane-3α,17β-diol (3α-adiol), 5α-androstane-3β,17β-diol (3β-adiol), the glucuronide or sulfate conjugate of 5-adiol and 3α-adiol were measured and observed to be dramatically reduced after NADT. By comparing patients that took leuprolide acetate alone vs leuprolide acetate plus abiraterone acetate and prednisone, we were able to distinguish the primary sources of these androgens and their conjugates as being of either testicular or adrenal in origin. We find that testosterone, 5α-dihydrotestosterone (DHT), 3α-adiol and 3β-adiol were predominately of testicular origin. By contrast, dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA), epi-androsterone (epi-AST) and their conjugates, 5-adiol sulfate and glucuronide were predominately of adrenal origin. Our findings also show that NADT failed to completely suppress DHEA-sulfate levels and that two unappreciated sources of intratumoral androgens that were not suppressed by leuprolide acetate alone were 5-adiol-sulfate and epi-AST-sulfate of adrenal origin.
Keywords: abiraterone acetate; androgen; localized high-risk prostate cancer; luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone agonist; stable isotope dilution liquid chromatography mass spectrometry.
© 2017 Society for Endocrinology.
Figures
References
-
- Aus G, Abrahamsson PA, Ahlgren G, Hugosson J, Lundberg S, Schain M, Schelin S, Pedersen K. Three-month neoadjuvant hormonal therapy before radical prostatectomy: a 7-year follow-up of a randomized controlled trial. BJU International. 2002;90:561–566. doi: 10.1046/j.1464-410X.2002.02982.x. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Barbier O, Lapointe H, El Alfy M, Hum DW, Belanger A. Cellular localization of uridine diphosphoglucuronosyltransferase 2B enzymes in the human prostate by in situ hybridization and immunohistochemistry. Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism. 2000;85:4819–4826. doi: 10.1210/jc.85.12.4819. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

