How Common Is Signal-Intensity Increase in Optic Nerve Segments on 3D Double Inversion Recovery Sequences in Visually Asymptomatic Patients with Multiple Sclerosis?
- PMID: 28663263
- PMCID: PMC7963692
- DOI: 10.3174/ajnr.A5262
How Common Is Signal-Intensity Increase in Optic Nerve Segments on 3D Double Inversion Recovery Sequences in Visually Asymptomatic Patients with Multiple Sclerosis?
Abstract
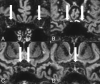
Background and purpose: In postmortem studies, subclinical optic nerve demyelination is very common in patients with MS but radiologic demonstration is difficult and mainly based on STIR T2WI. Our aim was to evaluate 3D double inversion recovery MR imaging for the detection of subclinical demyelinating lesions within optic nerve segments.
Materials and methods: The signal intensities in 4 different optic nerve segments (ie, retrobulbar, canalicular, prechiasmatic, and chiasm) were evaluated on 3D double inversion recovery MR imaging in 95 patients with MS without visual symptoms within the past 3 years and in 50 patients without optic nerve pathology. We compared the signal intensities with those of the adjacent lateral rectus muscle. The evaluation was performed by a student group and an expert neuroradiologist. Statistical evaluation (the Cohen κ test) was performed.
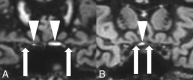
Results: On the 3D double inversion recovery sequence, optic nerve segments in the comparison group were all hypointense, and an isointense nerve sheath surrounded the retrobulbar nerve segment. At least 1 optic nerve segment was isointense or hyperintense in 68 patients (72%) in the group with MS on the basis of the results of the expert neuroradiologist. Student raters were able to correctly identify optic nerve hypersignal in 97%.
Conclusions: A hypersignal in at least 1 optic nerve segment on the 3D double inversion recovery sequence compared with hyposignal in optic nerve segments in the comparison group was very common in visually asymptomatic patients with MS. The signal-intensity rating of optic nerve segments could also be performed by inexperienced student readers.
© 2017 by American Journal of Neuroradiology.
Figures

References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
