Heavy+light chain monitoring correlates with clinical outcome in multiple myeloma patients
- PMID: 28663581
- PMCID: PMC5808078
- DOI: 10.1038/leu.2017.209
Heavy+light chain monitoring correlates with clinical outcome in multiple myeloma patients
Abstract
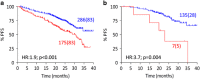
Novel anti-myeloma agents have improved patient response rates, which are historically based on reductions of the M-protein. These methods can be inaccurate for quantifying M-proteins at low concentrations. We compared the consistency and clinical impact of response assignment by electrophoretic and heavy+light chain (HLC) immunoassays post-consolidation in 463 newly diagnosed patients. The two methods gave similar assignments in patients with partial (PR; 79% agreement) or complete response (⩾CR; 92%). However, in patients achieving very good PR (VGPR) there was poor concordance between methods (45%). Median progression-free survival (PFS) for standard VGPR patients was 34.5 months; HLC responses stratified these patients further into PR, VGPR and ⩾CR, with median PFS of 21.3, 28.9 months and not reached, respectively; P<0.001. At this time, abnormal HLC ratios had better concordance with multiparametric flow cytometry (sensitivity 10-4) (37 and 34% positive, respectively), compared to immunofixation (62% positive). In addition, HLC-pair suppression was identified in 38% of patients and associated with shorter PFS (30.6 months vs not reached; P<0.001). We conclude that HLC monitoring could augment electrophoretic assessments in patients achieving VGPR. The prognostic significance of HLC responses might partly depend on the patients' ability to recover their immune system, as determined by normalisation of HLC measurements.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures





References
-
- Attal M, Harousseau JL, Facon T, Guilhot F, Doyen C, Fuzibet JG et al. Single versus double autologous stem-cell transplantation for multiple myeloma. N Engl J Med 2003; 349: 2495–2502. - PubMed
-
- Lahuerta JJ, Mateos MV, Martinez-Lopez J, Rosinol L, Sureda A, de la Rubia J et al. Influence of pre- and post-transplantation responses on outcome of patients with multiple myeloma: sequential improvement of response and achievement of complete response are associated with longer survival. J Clin Oncol 2008; 26: 5775–5782. - PubMed
-
- van de Velde HJ, Liu X, Chen G, Cakana A, Deraedt W, Bayssas M. Complete response correlates with long-term survival and progression-free survival in high-dose therapy in multiple myeloma. Haematologica 2007; 92: 1399–1406. - PubMed
-
- Shah J, Blade J, Sonneveld P, Harousseau JL, Lantz K, Londhe A et al. Rapid early monoclonal protein reduction after therapy with bortezomib or bortezomib and pegylated liposomal doxorubicin in relapsed/refractory myeloma is associated with a longer time to progression. Cancer 2011; 117: 3758–3762. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

