Dexmedetomidine as an Anesthetic Adjuvant in Intracranial Surgery
- PMID: 28663612
- PMCID: PMC5490096
- DOI: 10.4103/0259-1162.194555
Dexmedetomidine as an Anesthetic Adjuvant in Intracranial Surgery
Abstract
Background: The basic principle of neuroanesthesia is to provide hemodynamic stability, provision of optimal operative conditions, maintenance of cerebral perfusion pressure, and cerebral oxygenation.
Aim: This study was undertaken to see the effect of dexmedetomidine infusion on hemodynamics and its ability to act as an anesthetic adjuvant in patients undergoing supratentorial tumor surgery.
Setting and design: Prospective randomized control double blind study.
Subjects and methods: In this study, we compared two groups with 25 patients in each group. Group C patients received saline infusion during surgery and 4 μg/kg of fentanyl intravenously (i.v.) at the induction and at pin head application. Group D patients received dexmedetomidine infusion during surgery at the rate of 0.4 μg/kg/h and 2 μg/kg of fentanyl i.v. at the induction and at pin head application.
Statistical analyses used: Parametric data were analyzed using Student's t-test. The categorical data were studied using Chi-squared test or Fisher's test as appropriate.
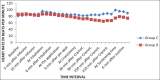
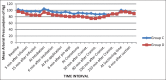
Results: The vitals remained within 20% of baseline in both groups during the study period except at the time of extubation where the rise in heart rate was more than 20% in control group. The requirement of thiopentone for induction was significantly less in dexmedetomidine group. In dexmedetomidine group, less number of patients required intraoperative fentanyl (P < 0.05), and the time to rescue analgesic was also more in Group D (P < 0.05).
Conclusion: Dexmedetomidine infusion started before surgery maintains hemodynamic stability intraoperatively and is effective in attenuating the cardiovascular responses to intubation, skull pin application, and extubation. It decreases the requirement of other anesthetic agents as well.
Keywords: Dexmedetomidine; hemodynamics; intracranial surgery.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The Effectiveness of Intravenous Dexmedetomidine on Perioperative Hemodynamics, Analgesic Requirement, and Side Effects Profile in Patients Undergoing Laparoscopic Surgery Under General Anesthesia.Anesth Essays Res. 2017 Jan-Mar;11(1):72-77. doi: 10.4103/0259-1162.200232. Anesth Essays Res. 2017. PMID: 28298760 Free PMC article.
-
Dexmedetomidine as an Anesthetic Adjuvant in Patients Undergoing Transsphenoidal Resection of Pituitary Tumor.J Neurosurg Anesthesiol. 2015 Jul;27(3):209-15. doi: 10.1097/ANA.0000000000000144. J Neurosurg Anesthesiol. 2015. PMID: 25493927 Clinical Trial.
-
Prospective, randomized controlled study to assess the role of dexmedetomidine in patients with supratentorial tumors undergoing craniotomy under general anesthesia.Middle East J Anaesthesiol. 2011 Feb;21(1):23-33. Middle East J Anaesthesiol. 2011. PMID: 21991729 Clinical Trial.
-
Prospective, randomized study to assess the role of dexmedetomidine in patients with supratentorial tumors undergoing craniotomy under general anaesthesia.Middle East J Anaesthesiol. 2011 Oct;21(3):325-34. Middle East J Anaesthesiol. 2011. PMID: 22428485 Clinical Trial.
-
The effects of intravenous dexmedetomidine on hemodynamic response in patients undergoing skull-pin head-holder application during neurosurgery - A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2020 Aug;195:105939. doi: 10.1016/j.clineuro.2020.105939. Epub 2020 May 20. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2020. PMID: 32480196
Cited by
-
Effect of a low-dose dexmedetomidine infusion on intraoperative hemodynamics, anesthetic requirements and recovery profile in patients undergoing lumbar spine surgery.J Anaesthesiol Clin Pharmacol. 2019 Apr-Jun;35(2):248-253. doi: 10.4103/joacp.JOACP_338_18. J Anaesthesiol Clin Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 31303717 Free PMC article.
-
Opioid-free anesthesia in enhanced recovery after supratentorial craniotomies: a case series.J Med Life. 2024 Dec;17(12):1061-1066. doi: 10.25122/jml-2024-0280. J Med Life. 2024. PMID: 39877039 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy of Dexmedetomidine versus Propofol in Patients Undergoing Endoscopic Transnasal Transsphenoidal Pituitary Tumor Resection.Anesth Essays Res. 2021 Oct-Dec;15(4):368-374. doi: 10.4103/aer.aer_154_21. Epub 2022 Mar 1. Anesth Essays Res. 2021. PMID: 35422551 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of anesthesia on cerebral blood flow, metabolism, and neuroprotection.J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2018 Dec;38(12):2192-2208. doi: 10.1177/0271678X18789273. Epub 2018 Jul 16. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2018. PMID: 30009645 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Efficacy of Dexmedetomidine Infusion Without Loading Dose on Hemodynamic Variables and Recovery Time During Craniotomy: A Randomized Double-blinded Controlled Study.Anesth Pain Med. 2021 May 2;11(2):e113410. doi: 10.5812/aapm.113410. eCollection 2021 Apr. Anesth Pain Med. 2021. PMID: 34336625 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ebert TJ, Hall JE, Barney JA, Uhrich TD, Colinco MD. The effects of increasing plasma concentrations of dexmedetomidine in humans. Anesthesiology. 2000;93:382–94. - PubMed
-
- Nakamura M, Ferreira SH. Peripheral analgesic action of clonidine: Mediation by release of endogenous enkephalin-like substances. Eur J Pharmacol. 1988;146:223–8. - PubMed
-
- Aho M, Erkola O, Kallio A, Scheinin H, Korttila K. Dexmedetomidine infusion for maintenance of anesthesia in patients undergoing abdominal hysterectomy. Anesth Analg. 1992;75:940–6. - PubMed
-
- Scheinin B, Lindgren L, Randell T, Scheinin H, Scheinin M. Dexmedetomidine attenuates sympathoadrenal responses to tracheal intubation and reduces the need for thiopentone and preoperative fentanyl. Br J Anaesth. 1992;68:126–31. - PubMed
-
- Lawrence CJ, De Lange S. Effects of a single pre-operative dexmedetomidine dose on isoflurane requirements and peri-operative haemodynamic stability. Anaesthesia. 1997;52:736–44. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources