Fully automatic acute ischemic lesion segmentation in DWI using convolutional neural networks
- PMID: 28664034
- PMCID: PMC5480013
- DOI: 10.1016/j.nicl.2017.06.016
Fully automatic acute ischemic lesion segmentation in DWI using convolutional neural networks
Abstract
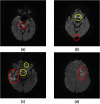
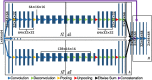
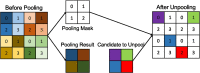
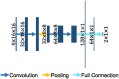
Stroke is an acute cerebral vascular disease, which is likely to cause long-term disabilities and death. Acute ischemic lesions occur in most stroke patients. These lesions are treatable under accurate diagnosis and treatments. Although diffusion-weighted MR imaging (DWI) is sensitive to these lesions, localizing and quantifying them manually is costly and challenging for clinicians. In this paper, we propose a novel framework to automatically segment stroke lesions in DWI. Our framework consists of two convolutional neural networks (CNNs): one is an ensemble of two DeconvNets (Noh et al., 2015), which is the EDD Net; the second CNN is the multi-scale convolutional label evaluation net (MUSCLE Net), which aims to evaluate the lesions detected by the EDD Net in order to remove potential false positives. To the best of our knowledge, it is the first attempt to solve this problem and using both CNNs achieves very good results. Furthermore, we study the network architectures and key configurations in detail to ensure the best performance. It is validated on a large dataset comprising clinical acquired DW images from 741 subjects. A mean accuracy of Dice coefficient obtained is 0.67 in total. The mean Dice scores based on subjects with only small and large lesions are 0.61 and 0.83, respectively. The lesion detection rate achieved is 0.94.
Keywords: Acute ischemic lesion segmentation; Convolutional neural networks; DWI; Deep learning.
Figures

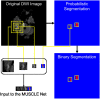

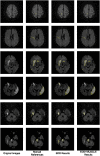
References
-
- Avendi M., Kheradvar A., Jafarkhani H. A combined deep-learning and deformable-model approach to fully automatic segmentation of the left ventricle in cardiac MRI. Med. Image Anal. 2016;30:108–119. - PubMed
-
- Bengio Y., Courville A., Vincent P. Representation learning: a review and new perspectives. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2013;35(8):1798–1828. - PubMed
-
- Chang P.D. Proceedings of MICCAI-BRATS 2016 Multimodal Brain Tumor Image Segmentation Benchmark: “Change Detection”. 2016. Fully convolutional neural networks with hyperlocal features for brain tumor segmentation; pp. 4–9.
-
- Charoensuk W., Covavisaruch N., Lerdlum S., Likitjaroen Y. Acute stroke brain infarct segmentation in DWI images. Int. J. Pharm. Med. Biol. Sci. 2015;4:115.
-
- Chen H., Qi X., Yu L., Heng P.A. 2016. DCAN: Deep Contour-Aware Networks for Accurate Gland Segmentation. (arXiv preprint arXiv:1604.02677) - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

