Physiological effects of formulation containing tannase-converted green tea extract on skin care: physical stability, collagenase, elastase, and tyrosinase activities
- PMID: 28664075
- PMCID: PMC5481706
- DOI: 10.1016/j.imr.2013.12.003
Physiological effects of formulation containing tannase-converted green tea extract on skin care: physical stability, collagenase, elastase, and tyrosinase activities
Abstract
Background: Green tea contains numerous polyphenols, which have health-promoting effects. The purpose of this study was to evaluate the effect of tannase-converted green tea extract (TGE) formulation on the physical stability and activities of skin-related enzymes.
Methods: Physical stability was evaluated by measuring the pH, precipitation, and colors at 25 ± 2 °C/ambient humidity and at 40 ± 2 °C/70% ± 5% relative humidity for 4 months. Activities of collagenase, elastase, and tyrosinase as skin-related enzymes were assessed on TGE formulation.
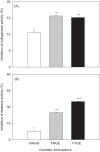
Results: The concentrations of epigallocatechin-3-gallate and epicatechin-3-gallate in green tea extract were greatly decreased to the extent of negligible level when treated with tannase. The formulation containing 5% tannase-converted green tea extract showed relatively stable pH, precipitation, and color features for 16 weeks. When TGE was added to the formulation, there was a significant increase in the inhibition of elastase and tyrosinase activities (p < 0.05) compared with the formulation containing 5% normal green tea extract.
Conclusion: The TGE could be used in cosmetics as skin antiwrinkling or depigmenting agent.
Keywords: elastase; green tea; stability; tannase; tyrosinase.
Figures





References
-
- Makrantonaki E., Zouboulis C.C. Skin alterations and diseases in advanced age. Drug Discov Today Dis Mech. 2008;5:e153–e162.
-
- Morganti P. Reflections on cosmetics, cosmeceuticals, and nutraceuticals. Clin Dermatol. 2008;26:318–320. - PubMed
-
- Gao X.H., Zhang L., Wei H., Chen H.D. Efficacy and safety of innovative cosmeceuticals. Clin Dermatol. 2008;26:367–374. - PubMed
-
- Rababah T.M., Hettiarachchy N.S., Horax R. Total phenolics and antioxidant activities of fenugreek, green tea, black tea, grape seed, ginger, rosemary, gotu kola, and ginkgo extracts, vitamin E, and tert-butylhydroquinone. J Agric Food Chem. 2004;52:5183–5186. - PubMed
-
- Rice-Evans C.A., Miller N.J. Antioxidant activities of flavonoids as bioactive components of food. Biochem Soc Trans. 1996;24:790–794. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

