Hematological parameters and all-cause mortality: a prospective study of older people
- PMID: 28664457
- PMCID: PMC5911276
- DOI: 10.1007/s40520-017-0791-y
Hematological parameters and all-cause mortality: a prospective study of older people
Abstract
Background: The effect of low and high concentration of some hematological parameters in the blood can have a negative impact on health.
Aim: Therefore, we investigated the associations between hematological parameters and all-cause mortality among older people living in Poland.
Methods: The study was carried out among 75-80-year-old participants (n = 403) from Warsaw and Olsztyn regions, Poland. Information on lifestyle factors and food consumption were obtained at baseline (June 1, 1999) using a self-administered questionnaire. Red blood cell, haemoglobin, hematocrit, mean corpuscular volume (MCV), mean corpuscular haemoglobin (MCH), and mean corpuscular haemoglobin concentration (MCHC) were determined. The data on deaths from all-causes were collected from the baseline until October 31, 2006. During an average of 7.4 years of follow-up, we ascertained 154 cases of death from all-causes.
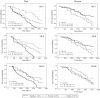
Results: Compared with men in the lowest tertile of MCV, MCH, and MCHC, the multivariable hazard ratios (HRs) of all-cause mortality in those in the highest tertile were 0.35 (95% CI, 0.17-0.73), 0.32 (95% CI, 0.16-0.67), and 0.44 (95% CI, 0.22-0.88), respectively. In contrast, among women after combining the second and the third tertiles of MCV, MCH, and MCHC, the HRs were 2.01 (95% CI, 1.01-3.99), 1.71 (95% CI, 0.85-3.43), and 1.09 (95% CI, 0.62-1.94), respectively.
Discussion/conclusion: We observed inverse associations between some hematological parameters and all-cause mortality among men, but not among women. This may be explained by a difference in iron metabolism, iron status, hormone regulations, or the occurrence of some diseases.
Keywords: Gender; Hematological parameters; Mortality; Older people; Prospective study.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest
None of the authors have any potential conflicts of interest to declare.
Human and animal rights
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical