Corticosterone influences gerbil (Meriones unguiculatus) prostatic morphophysiology and alters its proliferation and apoptosis rates
- PMID: 28664583
- PMCID: PMC5573771
- DOI: 10.1111/iep.12232
Corticosterone influences gerbil (Meriones unguiculatus) prostatic morphophysiology and alters its proliferation and apoptosis rates
Abstract
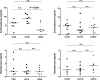
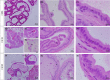
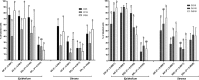
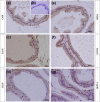
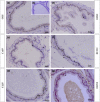
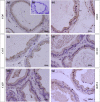
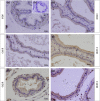
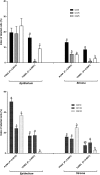
Glucocorticoids (GCs) are hormones that are widely used in medicine; but although side effects are generally recognised, little is known about the precise mechanisms that is implicated in many of these side effects. Furthermore, GCs are highly correlated with stress and behaviour disorders. This study evaluated the effects of the glucocorticoid corticosterone on the ventral prostate of the Mongolian gerbil. Male gerbils (Meriones unguiculatus) (n = 5) received intraperitoneal injections of saline or corticosterone in doses of 0.5 mg/kg/day and 1.5 mg/kg/day for 5 days; while some of the animals were killed immediately after the treatment, the others were killed 5 days after the treatment period. The data show that corticosterone influences the structure and functionality of this organ. This hormone has anti-proliferative and anti-apoptotic properties in the prostate. In addition, the frequencies of the androgen (AR), oestrogen (ERα, ERβ) and glucocorticoid (GR) receptors changed. The frequencies of AR, GR and ERβ decreased in the Ct1/5 group; in the groups with rest period, the frequencies of GR increased and ERβ decreased in the epithelium. Changes in the proliferative index, apoptotic index and receptor activity may have contributed to the emergence of prostatic morphological alterations, such as the presence of cellular debris and inflammatory cells. Different doses of corticosterone had variable effects on the prostate, with a higher dose showing subtler effects and a lower dose showing more striking effects. The corticosterone effects on nuclear receptors were reverted or attenuated after a rest period, which was not observed for proliferation and apoptosis. In summary, we have demonstrated that corticosterone might influence the prostatic morphophysiology and that these changes may be linked in some way to the altered receptor distribution.
Keywords: corticosterone; gerbil; glucocorticoids; ventral prostate.
© 2017 The Authors. International Journal of Experimental Pathology © 2017 International Journal of Experimental Pathology.
Figures


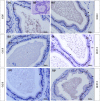
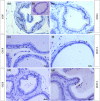
References
-
- Andersen ML, Ribeiro DA, Bergamaschi CT et al (2009) Distinct effects of acute and chronic sleep loss on DNA damage in rats. Prog.Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 33, 562–567. - PubMed
-
- Behmer A.O., Tolosa E.M.C. & Neto A.G.F. (1976) Manual de praticas para histologia normal e patologica. São Paulo, Brazil: Edart‐Edusp.
-
- Bland R., Worker C.A., Noble B.S. et al (1999) Characterization of 11b‐hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase activity and corticosteroid receptor expression in human osteosarcoma cell lines. J. Endocrinol. 161, 455–464. - PubMed
-
- Bruni‐Cardoso A., Vilamaior P.S., Taboga S.R. & Carvalho H.F. (2008) Localized matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)‐2 and MMP‐9 activity in the rat ventral prostate during the first week of postnatal development. Histochem. Cell Biol. 129(6), 805–815. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

