Treatment with low dose fasudil for acute ischemic stroke in chronic hypertension
- PMID: 28665172
- PMCID: PMC5584704
- DOI: 10.1177/0271678X17718665
Treatment with low dose fasudil for acute ischemic stroke in chronic hypertension
Abstract
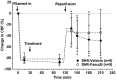
We investigated the effect of Rho kinase inhibition on changes in cerebral blood flow (CBF), brain injury and vascular function after ischemic stroke in spontaneously hypertensive rats (SHR). Changes in core MCA and collateral perfusion were measured by a validated laser Doppler method. Animals underwent 2 h tMCAO and 2 h reperfusion. Fasudil (0.1 mg/kg, i.v.) or vehicle was given at 30 min ischemia (n = 9/group; mean (SD)). Brain injury was determined by 2,3,5-triphenyltetrazolium chloride staining. To determine the effect of fasudil on vascular function, fasudil was given 10 min before reperfusion and parenchymal arterioles studied isolated (n = 6/group; mean(SD)). Collateral perfusion was low in vehicle-treated SHR (-8(32)%) that changed minimally with fasudil (6(24)%, p > 0.05, effect size: 0.47;95% CI-0.49-1.39). Reperfusion CBF was below baseline in vehicle (-27(26)%) and fasudil (-32(25)%, p > 0.05, effect size: 0.19; 95% CI-0.74-1.11) groups, suggesting incomplete reperfusion in both groups. Fasudil had little effect on brain injury volume (28(13)% vs. 36(7)% in vehicle, p > 0.05, effect size: 0.75; 95% CI-0.24-1.66). In isolated parenchymal arterioles, myogenic tone was similar between groups (37(6)% vs. 38(10)% in vehicle, p > 0.05, effect size: 0.09; 95% CI-1.05-1.21). There were no differences with fasudil treatment vs. vehicle in perfusion, brain injury and vascular function that may be related to the low dose that had minimal blood pressure lowering effect.
Keywords: Acute stroke; animal models; cerebral blood flow; focal ischemia; hypertension.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Vasodilator effects of fasudil, a Rho-kinase inhibitor, on retinal arterioles in stroke-prone spontaneously hypertensive rats.J Ocul Pharmacol Ther. 2007 Jun;23(3):207-12. doi: 10.1089/jop.2006.128. J Ocul Pharmacol Ther. 2007. PMID: 17593003
-
Inhibition of Rho-kinase attenuates nephrosclerosis and improves survival in salt-loaded spontaneously hypertensive stroke-prone rats.J Hypertens. 2007 May;25(5):1053-63. doi: 10.1097/HJH.0b013e3280825440. J Hypertens. 2007. PMID: 17414670
-
Inhibition of PAI (Plasminogen Activator Inhibitor)-1 Improves Brain Collateral Perfusion and Injury After Acute Ischemic Stroke in Aged Hypertensive Rats.Stroke. 2018 Aug;49(8):1969-1976. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.118.022056. Stroke. 2018. PMID: 29991657 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of fasudil on pulmonary hypertension in clinical practice.Pulm Pharmacol Ther. 2017 Oct;46:54-63. doi: 10.1016/j.pupt.2017.08.002. Epub 2017 Aug 4. Pulm Pharmacol Ther. 2017. PMID: 28782712 Review.
-
[Role of the Rho/Rho-kinase pathway in the development of hypertensive glomerulosclerosis: renoprotective effect of Rho-kinase inhibitor in hypertensive glomerulosclerosis and its molecular mechanism].Nihon Yakurigaku Zasshi. 2006 Sep;128(3):153-9, 152. doi: 10.1254/fpj.128.153. Nihon Yakurigaku Zasshi. 2006. PMID: 16971778 Review. Japanese. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Exome sequencing implicates ancestry-related Mendelian variation at SYNE1 in childhood-onset essential hypertension.JCI Insight. 2024 May 8;9(9):e172152. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.172152. JCI Insight. 2024. PMID: 38716726 Free PMC article.
-
Fasudil inhibits hepatic artery spasm by repressing the YAP/ERK/ ETA/ETB signaling pathway via inhibiting ROCK activation.Aging (Albany NY). 2022 Sep 19;14(18):7378-7389. doi: 10.18632/aging.204233. Epub 2022 Sep 19. Aging (Albany NY). 2022. PMID: 36126209 Free PMC article.
-
The synthesis and bioactivities of ROCK2 inhibitors with 1,2-dithiolan-3-yl motif.RSC Med Chem. 2024 Aug 1;15(10):3576-96. doi: 10.1039/d4md00438h. Online ahead of print. RSC Med Chem. 2024. PMID: 39268077 Free PMC article.
-
A new era for stroke therapy: Integrating neurovascular protection with optimal reperfusion.J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2018 Dec;38(12):2073-2091. doi: 10.1177/0271678X18798162. Epub 2018 Sep 7. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2018. PMID: 30191760 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Emerging neuroprotective strategies for the treatment of ischemic stroke: An overview of clinical and preclinical studies.Exp Neurol. 2021 Jan;335:113518. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2020.113518. Epub 2020 Nov 2. Exp Neurol. 2021. PMID: 33144066 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Wolf PA, D'Agostino RB, Belanger AJ, et al. Probability of stroke: a risk profile from the Framingham study. Stroke 1991; 22: 312–318. - PubMed
-
- O'Donnell MJ, Xavier D, Liu L, et al. Risk factors for ischaemic and intracerebral haemorrhagic stroke in 22 countries (the Interstroke study): a case-control study. Lancet 2010; 376: 112–123. - PubMed
-
- Leonardi-Bee J, Bath PM, Phillips SJ, et al. Blood pressure and clinical outcomes in the international stroke trial. Stroke 2002; 33: 1315–1320. - PubMed
-
- Paciaroni M, Agnelli G, Corea F, et al. Early hemorrhagic transformation of brain infarction: rate, predictive factors, and influence on clinical outcome: results of a prospective multicenter study. Stroke 2008; 39: 2249–2256. - PubMed
-
- Willmot M, Leonardi-Bee J, Bath PM. High blood pressure in acute stroke and subsequent outcome: a systematic review. Hypertension 2004; 43: 18–24. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

