Human embryonic lung epithelial tips are multipotent progenitors that can be expanded in vitro as long-term self-renewing organoids
- PMID: 28665271
- PMCID: PMC5555721
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.26575
Human embryonic lung epithelial tips are multipotent progenitors that can be expanded in vitro as long-term self-renewing organoids
Abstract
The embryonic mouse lung is a widely used substitute for human lung development. For example, attempts to differentiate human pluripotent stem cells to lung epithelium rely on passing through progenitor states that have only been described in mouse. The tip epithelium of the branching mouse lung is a multipotent progenitor pool that self-renews and produces differentiating descendants. We hypothesized that the human distal tip epithelium is an analogous progenitor population and tested this by examining morphology, gene expression and in vitro self-renewal and differentiation capacity of human tips. These experiments confirm that human and mouse tips are analogous and identify signalling pathways that are sufficient for long-term self-renewal of human tips as differentiation-competent organoids. Moreover, we identify mouse-human differences, including markers that define progenitor states and signalling requirements for long-term self-renewal. Our organoid system provides a genetically-tractable tool that will allow these human-specific features of lung development to be investigated.
Keywords: alveolar differentiation; branching; developmental biology; human; human biology; lung development; medicine; stem cell; stem cells; tip progenitor.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that no competing interests exist.
Figures
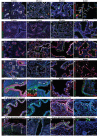

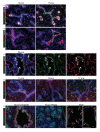
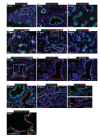
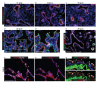

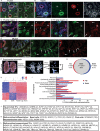
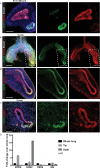
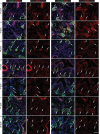
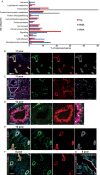
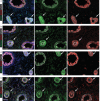

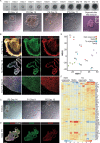
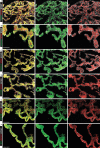


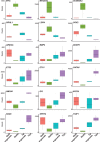

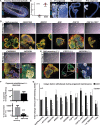

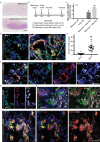

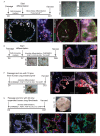
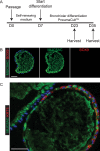



Comment in
-
Tips from the embryonic lung.Elife. 2017 Aug 14;6:e30194. doi: 10.7554/eLife.30194. Elife. 2017. PMID: 28806170 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Al Alam D, El Agha E, Sakurai R, Kheirollahi V, Moiseenko A, Danopoulos S, Shrestha A, Schmoldt C, Quantius J, Herold S, Chao CM, Tiozzo C, De Langhe S, Plikus MV, Thornton M, Grubbs B, Minoo P, Rehan VK, Bellusci S. Evidence for the involvement of fibroblast growth factor 10 in lipofibroblast formation during embryonic lung development. Development. 2015;142:4139–4150. doi: 10.1242/dev.109173. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bellusci S, Henderson R, Winnier G, Oikawa T, Hogan BL. Evidence from normal expression and targeted misexpression that bone morphogenetic protein (Bmp-4) plays a role in mouse embryonic lung morphogenesis. Development. 1996;122:1693–1702. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

