High-frequency oscillations: The state of clinical research
- PMID: 28666056
- PMCID: PMC5806699
- DOI: 10.1111/epi.13829
High-frequency oscillations: The state of clinical research
Abstract
Modern electroencephalographic (EEG) technology contributed to the appreciation that the EEG signal outside the classical Berger frequency band contains important information. In epilepsy, research of the past decade focused particularly on interictal high-frequency oscillations (HFOs) > 80 Hz. The first large application of HFOs was in the context of epilepsy surgery. This is now followed by other applications such as assessment of epilepsy severity and monitoring of antiepileptic therapy. This article reviews the evidence on the clinical use of HFOs in epilepsy with an emphasis on the latest developments. It highlights the growing literature on the association between HFOs and postsurgical seizure outcome. A recent meta-analysis confirmed a higher resection ratio for HFOs in seizure-free versus non-seizure-free patients. Residual HFOs in the postoperative electrocorticogram were shown to predict epilepsy surgery outcome better than preoperative HFO rates. The review further discusses the different attempts to separate physiological from epileptic HFOs, as this might increase the specificity of HFOs. As an example, analysis of sleep microstructure demonstrated a different coupling between HFOs inside and outside the epileptogenic zone. Moreover, there is increasing evidence that HFOs are useful to measure disease activity and assess treatment response using noninvasive EEG and magnetoencephalography. This approach is particularly promising in children, because they show high scalp HFO rates. HFO rates in West syndrome decrease after adrenocorticotropic hormone treatment. Presence of HFOs at the time of rolandic spikes correlates with seizure frequency. The time-consuming visual assessment of HFOs, which prevented their clinical application in the past, is now overcome by validated computer-assisted algorithms. HFO research has considerably advanced over the past decade, and use of noninvasive methods will make HFOs accessible to large numbers of patients. Prospective multicenter trials are awaited to gather information over long recording periods in large patient samples.
Keywords: Biomarker; Scalp EEG; Seizure; Sleep; Surgical outcome.
Wiley Periodicals, Inc. © 2017 International League Against Epilepsy.
Figures
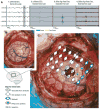

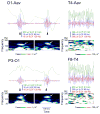
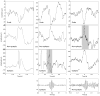
References
-
- Bragin A, Engel J, Jr, Wilson CL, et al. High-frequency oscillations in human brain. Hippocampus. 1999;9:137–142. - PubMed
-
- Zijlmans M, Worrell GA, Dümpelmann M. How to record high-frequency oscillations in epilepsy: A practical guideline. Epilepsia. 2017:58. https://doi.org/10.1111/epi.13814. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Allen PJ, Fish DR, Smith SJ. Very high-frequency rhythmic activity during SEEG suppression in frontal lobe epilepsy. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1992;82:155–159. - PubMed
-
- Fisher RS, Webber WR, Lesser RP, et al. High-frequency EEG activity at the start of seizures. J Clin Neurophysiol. 1992;9:441–448. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

