The Contribution of Inflammation to the Development of Hypertension Mediated by Increased Arterial Stiffness
- PMID: 28666991
- PMCID: PMC5586296
- DOI: 10.1161/JAHA.117.005729
The Contribution of Inflammation to the Development of Hypertension Mediated by Increased Arterial Stiffness
Abstract
Background: The mechanisms underlying the possible contribution of chronic inflammation to the development of hypertension remain unclear. We examined the longitudinal association of inflammation with the progression of vascular and/or renal abnormalities in the development of hypertension.
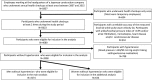
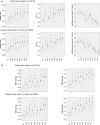
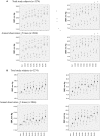
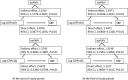
Methods and results: In 3274 middle-aged Japanese men without hypertension at the study baseline, brachial-ankle pulse wave velocity, blood pressure, estimated glomerular filtration rate, and serum CRP (C reactive protein) levels were measured annually during a 9-year period. During this study period, 474 participants (14.5%) developed hypertension. Analysis of the repeated-measures data revealed that sustained elevation of serum CRP levels was associated with a longitudinal increase of the brachial-ankle pulse wave velocity. A linear mixed model analysis revealed that higher log-transformed serum CRP values (log CRP) at each measurement were associated with a higher annual increase of the brachial-ankle pulse wave velocity (estimate=32.553±11.635 cm/s per log CRP, P=0.018), and that higher values of the brachial-ankle pulse wave velocity at each measurement were associated with a higher annual elevation of blood pressure (estimate=0.025±0.002 mm Hg per log CRP, P<0.001).
Conclusions: In middle-aged Japanese men without hypertension at study baseline, long-term active inflammation appears to be associated with a longitudinal increase of arterial stiffness. In turn, this longitudinal increase of arterial stiffness appears to be associated with longitudinal elevation of blood pressure to the hypertensive range. Thus, systemic inflammation may play a role in the pathogenesis of hypertension by the progression of arterial stiffness.
Keywords: C‐reactive protein; arterial stiffness; hypertension; inflammation.
© 2017 The Authors. Published on behalf of the American Heart Association, Inc., by Wiley.
Figures
References
-
- Rodríguez‐Iturbe B, Pons H, Quiroz Y, Lanaspa MA, Johnson RJ. Autoimmunity in the pathogenesis of hypertension. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2014;10:56–62. - PubMed
-
- Caillon A, Schiffrin EL. Role of inflammation and immunity in hypertension: recent epidemiological, laboratory, and clinical evidence. Curr Hypertens Rep. 2016;18:21. - PubMed
-
- Egan BM, Zhao Y, Axon RN. US trends in prevalence, awareness, treatment, and control of hypertension, 1988–2008. JAMA. 2010;303:2043–2050. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

