Regional heterogeneity in the mechanisms of myogenic tone in hamster arterioles
- PMID: 28667050
- PMCID: PMC5625173
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpheart.00183.2017
Regional heterogeneity in the mechanisms of myogenic tone in hamster arterioles
Abstract
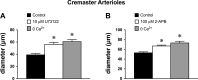
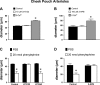
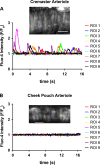
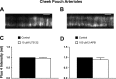
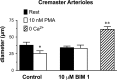
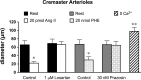
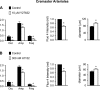
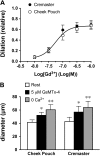
Myogenic tone is an important feature of arterioles and resistance arteries, but the mechanisms responsible for this hallmark characteristic remain unclear. We used pharmacological inhibitors to compare the roles played by phospholipase C (PLC; 10 μM U73122), inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptors (IP3Rs; 100 μM 2-aminoethoxydiphenylborane), protein kinase C (10 μM bisindolylmaleimide I), angiotensin II type 1 receptors (1 μM losartan), Rho kinase (10 nM-30 μM Y27632 or 300 nM H1152), stretch-activated ion channels (10 nM-1 μM Gd3+ or 5 μM spider venom toxin GsMTx-4) and L-type voltage-gated Ca2+ channels (0.3-100 μM diltiazem) in myogenic tone of cannulated, pressurized (80 cmH2O), second-order hamster cremaster or cheek pouch arterioles. Effective inhibition of either PLC or IP3Rs dilated cremaster arterioles, inhibited Ca2+ waves, and reduced global Ca2+ levels. In contrast, cheek pouch arterioles did not display Ca2+ waves and inhibition of PLC or IP3Rs had no effect on myogenic tone or intracellular Ca2+ levels. Inhibition of Rho kinase dilated both cheek pouch and cremaster arterioles with equal efficacy and potency but also reduced intracellular Ca2+ signals in both arterioles. Similarly, inhibition of mechanosensitive ion channels with Gd2+ or GsMTx-4 produced comparable dilation in both arterioles. Inhibition of L-type Ca2+ channels with diltiazem was more effective in dilating cremaster (86 ± 5% dilation, n = 4) than cheek pouch arterioles (54 ± 4% dilation, n = 6, P < 0.05). Thus, there are substantial differences in the mechanisms underlying myogenic tone in hamster cremaster and cheek pouch arterioles. Regional heterogeneity in myogenic mechanisms could provide new targets for drug development to improve regional blood flow in a tissue-specific manner.NEW & NOTEWORTHY Regional heterogeneity in the mechanisms of pressure-induced myogenic tone implies that resistance vessels may be able to alter myogenic signaling pathways to adapt to their environment. A better understanding of the spectrum of myogenic mechanisms could provide new targets to treat diseases that affect resistance artery and arteriolar function.
Keywords: arterioles; hamster; microcirculation; myogenic tone.
Copyright © 2017 the American Physiological Society.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Ion channels and the regulation of myogenic tone in peripheral arterioles.Curr Top Membr. 2020;85:19-58. doi: 10.1016/bs.ctm.2020.01.002. Epub 2020 Feb 25. Curr Top Membr. 2020. PMID: 32402640 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Voltage-gated Ca2+ channel activity modulates smooth muscle cell calcium waves in hamster cremaster arterioles.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2018 Oct 1;315(4):H871-H878. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00292.2018. Epub 2018 Jun 29. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2018. PMID: 29957015 Free PMC article.
-
Heterogeneous function of ryanodine receptors, but not IP3 receptors, in hamster cremaster muscle feed arteries and arterioles.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2011 May;300(5):H1616-30. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00728.2010. Epub 2011 Feb 25. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2011. PMID: 21357503 Free PMC article.
-
Longchain n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids and microvascular reactivity: observation in the hamster cheek pouch.Microvasc Res. 2007 May;73(3):237-47. doi: 10.1016/j.mvr.2006.11.002. Epub 2006 Dec 28. Microvasc Res. 2007. PMID: 17196224
-
Calcium-Dependent Ion Channels and the Regulation of Arteriolar Myogenic Tone.Front Physiol. 2021 Nov 8;12:770450. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2021.770450. eCollection 2021. Front Physiol. 2021. PMID: 34819877 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Ion channels and the regulation of myogenic tone in peripheral arterioles.Curr Top Membr. 2020;85:19-58. doi: 10.1016/bs.ctm.2020.01.002. Epub 2020 Feb 25. Curr Top Membr. 2020. PMID: 32402640 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of age, Rho-kinase 2 expression, and G protein-mediated signaling in the myogenic response in mouse small mesenteric arteries.Physiol Rep. 2018 Sep;6(17):e13863. doi: 10.14814/phy2.13863. Physiol Rep. 2018. PMID: 30198176 Free PMC article.
-
Statistical considerations in reporting cardiovascular research.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2018 Aug 1;315(2):H303-H313. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00309.2018. Epub 2018 Jul 20. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2018. PMID: 30028200 Free PMC article.
-
Vascular mechanotransduction.Physiol Rev. 2023 Apr 1;103(2):1247-1421. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00053.2021. Epub 2023 Jan 5. Physiol Rev. 2023. PMID: 36603156 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chemo-mechanical modeling of smooth muscle cell activation for the simulation of arterial walls under changing blood pressure.Biomech Model Mechanobiol. 2023 Jun;22(3):1049-1065. doi: 10.1007/s10237-023-01700-x. Epub 2023 Mar 9. Biomech Model Mechanobiol. 2023. PMID: 36892587 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abramoff MD, Magelhaes PJ, Ram SJ. Image processing with ImageJ. Biophoton Int 11: 36–42, 2004.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

