Increased activity of the orexin system in the paraventricular nucleus contributes to salt-sensitive hypertension
- PMID: 28667055
- PMCID: PMC5814649
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpheart.00822.2016
Increased activity of the orexin system in the paraventricular nucleus contributes to salt-sensitive hypertension
Abstract
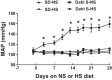
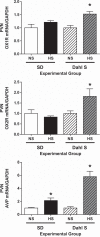
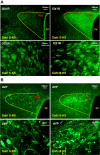
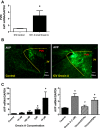
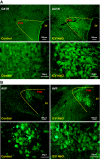
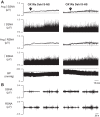
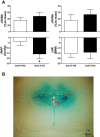
The orexin system is involved in arginine vasopressin (AVP) regulation, and its overactivation has been implicated in hypertension. However, its role in salt-sensitive hypertension (SSHTN) is unknown. Here, we tested the hypothesis that hyperactivity of the orexin system in the paraventricular nucleus (PVN) contributes to SSHTN via enhancing AVP signaling. Eight-week-old male Dahl salt-sensitive (Dahl S) and age- and sex-matched Sprague-Dawley (SD) rats were placed on a high-salt (HS; 8% NaCl) or normal-salt (NS; 0.4% NaCl) diet for 4 wk. HS intake did not alter mean arterial pressure (MAP), PVN mRNA levels of orexin receptor 1 (OX1R), or OX2R but slightly increased PVN AVP mRNA expression in SD rats. HS diet induced significant increases in MAP and PVN mRNA levels of OX1R, OX2R, and AVP in Dahl S rats. Intracerebroventricular infusion of orexin A (0.2 nmol) dramatically increased AVP mRNA levels and immunoreactivity in the PVN of SD rats. Incubation of cultured hypothalamus neurons from newborn SD rats with orexin A increased AVP mRNA expression, which was attenuated by OX1R blockade. In addition, increased cerebrospinal fluid Na+ concentration through intracerebroventricular infusion of NaCl solution (4 µmol) increased PVN OX1R and AVP mRNA levels and immunoreactivity in SD rats. Furthermore, bilateral PVN microinjection of the OX1R antagonist SB-408124 resulted in a greater reduction in MAP in HS intake (-16 ± 5 mmHg) compared with NS-fed (-4 ± 4 mmHg) anesthetized Dahl S rats. These results suggest that elevated PVN OX1R activation may contribute to SSHTN by enhancing AVP signaling.NEW & NOTEWORTHY To our best knowledge, this study is the first to investigate the involvement of the orexin system in salt-sensitive hypertension. Our results suggest that the orexin system may contribute to the Dahl model of salt-sensitive hypertension by enhancing vasopressin signaling in the hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus.
Keywords: orexin; paraventricular nucleus; salt-sensitive hypertension; sympathetic nerve activity; vasopressin.
Copyright © 2017 the American Physiological Society.
Figures

References
-
- Al-Barazanji KA, Wilson S, Baker J, Jessop DS, Harbuz MS. Central orexin-A activates hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis and stimulates hypothalamic corticotropin releasing factor and arginine vasopressin neurones in conscious rats. J Neuroendocrinol 13: 421–424, 2001. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2826.2001.00655.x. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

