Molecular docking studies on thirteen fluoroquinolines with human topoisomerase II a and b
- PMID: 28667488
- PMCID: PMC5493602
- DOI: 10.1007/s40203-017-0024-2
Molecular docking studies on thirteen fluoroquinolines with human topoisomerase II a and b
Abstract
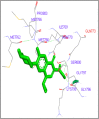
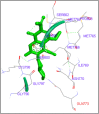
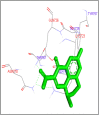
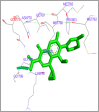
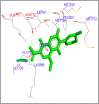
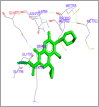
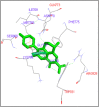
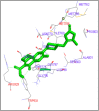
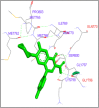
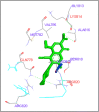
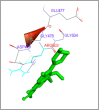
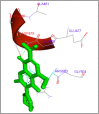
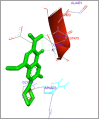
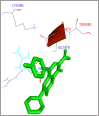
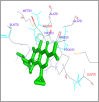
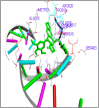
DNA relaxation is an important step in DNA replication. DNA topoisomerases play a major role in DNA relaxation. Hence these enzymes are important targets for cancer drugs. DNA topoisomerase inhibitors bind to the transient enzyme-DNA complex and inhibit DNA replication. Various inhibitors of topoisomerase I and II are prescribed as drugs. Topoisomerase II is considered as an important target for the development of anticancer drugs. In this study we have demonstrated molecular docking of thirteen fluoroquinolines with human DNA topoisomerase II alpha (a) and beta (b). Fluoroquinolines are broad spectrum antibacterial antibiotics and it is highly effective against various bacterial infections. Some of the fluoroquinolines like moxifloxacin exert antifungal as well as anti-cancer activity. It forms complexes with topoisomerase II a and are responsible for stoppage DNA replication. Molecular docking studies showed that fluoroquinolines has shown formation of hydrogen bond and good binding affinity with human Topo2a and Topo2b. Hence FQs may inhibit the activity of enzyme topoisomerase by binding at its active site. Ofloxacin, sparafloxacin, ciprofloxacin and moxifloxacin are predicted to be the most potent inhibitors among the thirteen FQs docked. GLN773, ASN770, LYS723 and TRP931 amino acid residues of Topo2a are involved in binding with FQs while ASP479, SER480, ARG820, ARG503, LYS456 and GLN778 amino acid residues of Topo2b are involved in binding with FQs. Our in silico study suggests that fluoroquinolines could be repositioned as DNA topoisomerase II inhibitors hence can be used as anticancer drugs. In vitro and in vivo experiments need to be done to confirm their efficacy.
Keywords: Anticancer; Drug repositioning; Fluoroquinolines; Human DNA topoisomerase II; In silico; Molecular docking.
Figures












Similar articles
-
Topoisomerase II as a target for repurposed antibiotics in Candida albicans: an in silico study.In Silico Pharmacol. 2021 Mar 26;9(1):24. doi: 10.1007/s40203-021-00082-1. eCollection 2021. In Silico Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33868894 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Synthesis, in silico molecular docking analysis, pharmacokinetic properties and evaluation of antibacterial and antioxidant activities of fluoroquinolines.BMC Chem. 2022 Jan 13;16(1):1. doi: 10.1186/s13065-022-00795-0. BMC Chem. 2022. PMID: 35027086 Free PMC article.
-
The antibacterial agent, moxifloxacin inhibits virulence factors of Candida albicans through multitargeting.World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2017 May;33(5):96. doi: 10.1007/s11274-017-2264-z. Epub 2017 Apr 13. World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2017. PMID: 28409362
-
Molecular docking studies of curcumin natural derivatives with DNA topoisomerase I and II-DNA complexes.Interdiscip Sci. 2014 Dec;6(4):285-91. doi: 10.1007/s12539-012-0048-6. Epub 2014 Aug 9. Interdiscip Sci. 2014. PMID: 25118649
-
Review and Current Perspectives on DNA Topoisomerase I and II Enzymes of Fungi as Study Models for the Development of New Antifungal Drugs.J Fungi (Basel). 2024 Sep 3;10(9):629. doi: 10.3390/jof10090629. J Fungi (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39330389 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Norfloxacin Derivative with Carbazole at C-7 FQB-1 Induces Cytotoxic, Antiproliferative, and Antitumor Effects in an Experimental Lung Carcinoma Model.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2025 Apr 30;18(5):664. doi: 10.3390/ph18050664. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40430482 Free PMC article.
-
Antiproliferative and Enzyme Docking Analysis of Engleromycin from Engleromyces goetzei.Molecules. 2019 Jan 4;24(1):166. doi: 10.3390/molecules24010166. Molecules. 2019. PMID: 30621140 Free PMC article.
-
Design, synthesis, and biological evaluation of a small molecule oral agonist of the glucagon-like-peptide-1 receptor.J Biol Chem. 2022 May;298(5):101889. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2022.101889. Epub 2022 Apr 2. J Biol Chem. 2022. PMID: 35378127 Free PMC article.
-
Density Functional Theory, Chemical Reactivity, Pharmacological Potential and Molecular Docking of Dihydrothiouracil-Indenopyridopyrimidines with Human-DNA Topoisomerase II.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Feb 13;21(4):1253. doi: 10.3390/ijms21041253. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32070048 Free PMC article.
-
Structural Recognition and Binding Pattern Analysis of Human Topoisomerase II Alpha with Steroidal Drugs: In Silico Study to Switchover the Cancer Treatment.Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2020 May 1;21(5):1349-1355. doi: 10.31557/APJCP.2020.21.5.1349. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2020. PMID: 32458643 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bertozzi D, Marinello J, Manzo SG, Fornari F, Gramantieri L, Capranico G. The natural inhibitor of DNA topoisomerase I, camptothecin, modulates HIF-1α activity by changing miR expression patterns in human cancer cells. Mol Cancer Ther. 2014;13(1):239–248. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-13-0729. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

