Serum cytokine profile in pediatric Sweet's syndrome: a case report
- PMID: 28668093
- PMCID: PMC5494139
- DOI: 10.1186/s13256-017-1317-0
Serum cytokine profile in pediatric Sweet's syndrome: a case report
Abstract
Background: Sweet's syndrome is characterized by fever, leukocytosis, and tender erythematous papules or nodules. It is a rare condition, particularly in the pediatric population, and has recently been proposed to be an autoinflammatory disease that occurs due to innate immune system dysfunction, involving several cytokines, which causes abnormally increased inflammation. To the best of our knowledge, no report has documented the cytokine profile in a pediatric patient with Sweet's syndrome.
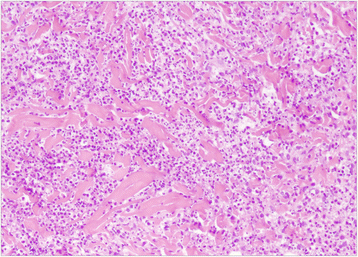
Case presentation: A previously healthy 34-month-old Japanese girl was hospitalized because of remittent fever and pain in her right lower extremity with erythematous nodules. A skin biopsy of the eruption revealed dermal perivascular neutrophilic infiltration with no evidence of vasculitis, which led to the diagnosis of Sweet's syndrome. She was prescribed with orally administered prednisolone and a prompt response was observed; then, the prednisolone dose was tapered. During treatment she developed upper and lower urinary tract infections, after which her cutaneous symptoms failed to improve despite increasing the prednisolone dosage. To avoid long-term use of systemic corticosteroids, orally administered potassium iodide was initiated, but it was unsuccessful. However, orally administered colchicine along with prednisolone effectively ameliorated her symptoms, and prednisolone dosage was reduced again. We analyzed the circulating levels of interleukin-1β, interleukin-6, interleukin-18, neopterin, and soluble tumor necrosis factor receptors I and II, in order to clarify the pathogenesis of Sweet's syndrome. Of these cytokines, only interleukin-6 levels were elevated prior to orally administered prednisolone therapy. Following therapy, the elevated interleukin-6 levels gradually diminished to almost normal levels; interleukin-1β and interleukin-18 stayed within normal ranges throughout the treatment. Neopterin became marginally elevated after the start of treatment. Both soluble tumor necrosis factor receptor I and soluble tumor necrosis factor receptor II levels increased shortly after the onset of urinary tract infections.
Conclusions: This is the first case report of pediatric Sweet's syndrome in which serum cytokine levels were investigated. Future studies should gather more evidence to elucidate the pathophysiology of Sweet's syndrome.
Keywords: Case report; Glucocorticoid resistance; Neutrophilic dermatosis; Pro-inflammatory cytokines; Sweet’s syndrome; Urinary tract infections.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Sweet's syndrome--a comprehensive review of an acute febrile neutrophilic dermatosis.Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2007 Jul 26;2:34. doi: 10.1186/1750-1172-2-34. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2007. PMID: 17655751 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sweet's syndrome: a review of current treatment options.Am J Clin Dermatol. 2002;3(2):117-31. doi: 10.2165/00128071-200203020-00005. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2002. PMID: 11893223 Review.
-
Cryptogenic organizing pneumonia in Sweet's syndrome: case report and review of the literature.Clin Respir J. 2016 Mar;10(2):250-4. doi: 10.1111/crj.12206. Epub 2014 Oct 2. Clin Respir J. 2016. PMID: 25196175 Review.
-
Neutrophilic Dermatosis of the Hands: A Case Report.Acta Dermatovenerol Croat. 2023 Dec;31(3):148-50. Acta Dermatovenerol Croat. 2023. PMID: 38439725
-
Sweet's syndrome with tendinitis.J Assoc Physicians India. 2005 Aug;53:728-30. J Assoc Physicians India. 2005. PMID: 16398086
Cited by
-
Tocilizumab-Induced Sweet Syndrome in a Familial Mediterranean Fever Patient: A Case Report.Dermatol Pract Concept. 2024 Jul 1;14(3):e2024190. doi: 10.5826/dpc.1403a190. Dermatol Pract Concept. 2024. PMID: 39122520 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Use of tocilizumab in amyloid a nephropathy associated with Sweet syndrome: a case report and literature review.CEN Case Rep. 2021 Feb;10(1):23-29. doi: 10.1007/s13730-020-00507-4. Epub 2020 Jul 17. CEN Case Rep. 2021. PMID: 32681397 Free PMC article.
-
Increase of a wide range of bioactive substances in an active phase of neuro-Sweet disease.BMJ Case Rep. 2020 Apr 8;13(4):e233457. doi: 10.1136/bcr-2019-233457. BMJ Case Rep. 2020. PMID: 32273270 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Characteristics of Sweet Syndrome: A Systematic Review.Exp Dermatol. 2024 Dec;33(12):e70022. doi: 10.1111/exd.70022. Exp Dermatol. 2024. PMID: 39704328 Free PMC article.
-
Cytokine Profile in Sweet's Syndrome under the Treatment of Pulmonary Toxoplasmosis Complicated with Myelodysplastic Syndrome.Intern Med. 2019 Jul 15;58(14):2079-2083. doi: 10.2169/internalmedicine.2372-18. Epub 2019 Mar 28. Intern Med. 2019. PMID: 30918190 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

