Pulmonary Clinicopathological Correlation after Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation: An Autopsy Series
- PMID: 28668489
- PMCID: PMC5797990
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbmt.2017.06.009
Pulmonary Clinicopathological Correlation after Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation: An Autopsy Series
Abstract
Pulmonary complications are a significant cause of morbidity, mortality, and resource utilization after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT). The objective of this study was to compare antemortem clinical suspicion of pulmonary complications and postmortem findings in a modern HSCT cohort. All patients who underwent allogeneic HSCT at our institution (n = 1854) between January 1, 2000 and June 30, 2010 were reviewed and patients who died of any cause greater than 1 year after HSCT and had an unrestricted autopsy available for analysis were included. Presence of pulmonary graft-versus-host disease (GVHD) was assessed by a pathologist blinded to the autopsy report, as previously described by Yousem (1995). A total of 35 (1.9%) patients had autopsies available for review. Airway disease, vascular disease, and interstitial disease were all clinically under-recognized compared with the pathological findings on autopsy. Varying degrees of pathological changes were detected, including 10 (28.6%) patients having bronchiolitis obliterans (BO) and 12 (34.3%) patients having pulmonary veno-occlusive disease (PVOD). Pulmonary manifestations of chronic GVHD, particularly BO and PVOD, were clinically under-recognized in our cohort. Our results suggest that PVOD, which has traditionally been considered a rare complication, may be clinically and histologically under-recognized.
Keywords: Autopsy; Graft-versus-host disease; Hematopoietic stem cell transplantation.
Copyright © 2017 The American Society for Blood and Marrow Transplantation. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
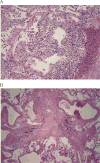

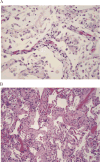
Comment in
-
Pulmonary Injury and Chronic Graft-versus-Host Disease: Do We Miss the Signs and Symptoms?Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2017 Oct;23(10):1605-1606. doi: 10.1016/j.bbmt.2017.08.015. Epub 2017 Aug 16. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2017. PMID: 28822829 No abstract available.
References
-
- Allareddy V, Roy A, Rampa S, Lee MK, Nalliah RP, Rotta AT. Outcomes of stem cell transplant patients with acute respiratory failure requiring mechanical ventilation in the United States. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2014;49:1278–1286. - PubMed
-
- Yanik G, Kitko C. Management of noninfectious lung injury following hematopoietic cell transplantation. Curr Opin Oncol. 2013;25:187–194. - PubMed
-
- Soubani AO, Pandya CM. The spectrum of noninfectious pulmonary complications following hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Hematol Oncol Stem Cell Ther. 2010;3:143–157. - PubMed
-
- Uhlving HH, Andersen CB, Christensen IJ, et al. Biopsy-verified bronchiolitis obliterans and other noninfectious lung pathologies after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2015;21:531–538. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

