Management of ulcerative colitis in Taiwan: consensus guideline of the Taiwan Society of Inflammatory Bowel Disease
- PMID: 28670225
- PMCID: PMC5478753
- DOI: 10.5217/ir.2017.15.3.266
Management of ulcerative colitis in Taiwan: consensus guideline of the Taiwan Society of Inflammatory Bowel Disease
Abstract
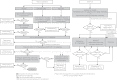
Ulcerative colitis (UC) is an inflammatory bowel disease characterized by chronic mucosal inflammation of the colon, and the prevalence and incidence of UC have been steadily increasing in Taiwan. A steering committee was established by the Taiwan Society of Inflammatory Bowel Disease to formulate statements on the diagnosis and management of UC taking into account currently available evidence and the expert opinion of the committee. Accurate diagnosis of UC requires thorough clinical, endoscopic, and histological assessment and careful exclusion of differential diagnoses, particularly infectious colitis. The goals of UC therapy are to induce and maintain remission, reduce the risk of complications, and improve quality of life. As outlined in the recommended treatment algorithm, choice of treatment is dictated by severity, extent, and course of disease. Patients should be evaluated for hepatitis B virus and tuberculosis infection prior to immunosuppressive treatment, especially with steroids and biologic agents, and should be regularly monitored for reactivation of latent infection. These consensus statements are also based on current local evidence with consideration of factors, and could be serve as concise and practical guidelines for supporting clinicians in the management of UC in Taiwan.
Keywords: Consensus statements; Disease management; Inflammatory bowel disease; Taiwan; Ulcerative colitis.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: None.
Figures

References
-
- Feuerstein JD, Cheifetz AS. Ulcerative colitis: epidemiology, diagnosis, and management. Mayo Clin Proc. 2014;89:1553–1563. - PubMed
-
- Molodecky NA, Soon IS, Rabi DM, et al. Increasing incidence and prevalence of the inflammatory bowel diseases with time, based on systematic review. Gastroenterology. 2012;142:46–54. - PubMed
-
- Cosnes J, Gower-Rousseau C, Seksik P, Cortot A. Epidemiology and natural history of inflammatory bowel diseases. Gastroenterology. 2011;140:1785–1794. - PubMed
-
- Chuang CH, Lin SH, Chen CY, Sheu BS, Kao AW, Wang JD. Increasing incidence and lifetime risk of inflammatory bowel disease in Taiwan: a nationwide study in a low-endemic area 1998-2010. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2013;19:2815–2819. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

