Valproic acid, targets papillary thyroid cancer through inhibition of c-Met signalling pathway
- PMID: 28670399
- PMCID: PMC5489911
Valproic acid, targets papillary thyroid cancer through inhibition of c-Met signalling pathway
Abstract
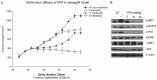
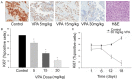
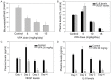
Tyrosine kinase receptors such as c-Met and its ligands are interesting therapeutic targets that have been reported to be involved in the progression of several types of cancers. Histone deacetylase inhibitor, valproic acid (VPA) is one such compound with promising anti-cancer properties. The current study was designed to evaluate the c-Met activity of VPA in thyroid carcinoma. A total 36 nu/nu mice with SW1736 cells-induced tumours were randomised into three treatment groups (5, 15, 30 mg/kg/day p.o. VPA; n = 9/group). Various cellular and enzymatic assays were performed to evaluate the dose-response relationship of VPA in c-Met inhibition. In vitro assays revealed that VPA (IC50, 5-26 nmol/l) shows c-Met phosphorylation and c-Met-dependent inhibition of cellproliferation. This causes inhibition of downstream signalling pathways in human thyroid cancer cell lines (SW1736, WRO). Additionally, VPA also showed anti-angiogenetic activity in HGF-stimulated endothelial cell. VPA showed significant reduction in tumour size in xenograft model (P = 0.023) with high levels of c-Met expression. The anticancer activity was found to be dose dependent and strongly correlated with c-Met expression. Thus, this novel finding paves way for investigation of new mechanism of action and its validation in clinical settings.
Keywords: RTK inhibitor; Thyroid cancer; c-Met signalling; papillary thyroid carcinoma; valproic acid.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures


References
-
- Blume-Jensen P, Hunter T. Oncogenic kinase signalling. Nature. 2001;411:355–365. - PubMed
-
- Schlessinger J. Cell signaling by receptor tyrosine kinases. Cell. 2000;103:211–225. - PubMed
-
- Baselga J. Targeting tyrosine kinases in cancer: the second wave. Science. 2006;312:1175–1178. - PubMed
-
- Christensen JG, Burrows J, Salgia R. c-Met as a target for human cancer and characterization of inhibitors for therapeutic intervention. Cancer Lett. 2005;225:1–26. - PubMed
-
- Bottaro DP, Rubin JS, Faletto DL, Chan AM, Kmiecik TE, Vande Woude GF, Aaronson SA. Identification of the hepatocyte growth factor receptor as the c-met proto-oncogene product. Science. 1991;251:802–804. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
