Radioactive Iodine Therapy and Glucose Tolerance
- PMID: 28670511
- PMCID: PMC5413587
- DOI: 10.22074/cellj.2016.4251
Radioactive Iodine Therapy and Glucose Tolerance
Abstract
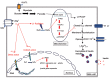
Radioactive iodine therapy is commonly used as an adjuvant therapy in follicular and papillary thyroid carcinoma (PTC) and in the treatment of Graves' disease (GD). The basis of this therapy is the accumulation of radioactive iodine by the sodium-iodide symporter (NIS) in the thyroid gland. Expression of NIS by extrathyroidal tissues such as islets of pancreas has been reported. Radioactive iodine uptake by pancreatic beta-cells can potentially damage these cells. In this study, we discuss the possible associations between radioactive iodine and glucose intolerance. Overall, radioactive iodine uptake by the pancreas may damage beta-cells and predispose patients to glucose intolerance or type 2 diabetes, particularly in patients exposed to radioactive iodine therapy following total thyroidectomy. Further studies are needed to clarify and confirm this association.
Keywords: Glucose Tolerance; Iodine; Pancreas; Radioactive; Sodium-Iodide Symporter.
Figures
References
-
- Sawin CT, Becker DV. Radioiodine and the treatment of hyperthyroidism: the early history. Thyroid. 1997;7(2):163–176. - PubMed
-
- Rivkees SA, Dinauer C. The use of 131 iodine in the treatment of Graves’ disease in children. In: Preedy VR, Burrow GN, Watson R, editors. Comprehensive handbook of iodine: nutritional, biochemical, pathological and therapeutic aspects. 1st ed. Boston: Academic Press; 2009. pp. 943–992.
-
- Gittoes NJ, Franklyn JA. Hyperthyroidism.Current treatment guidelines. Drugs. 1998;55(4):543–553. - PubMed
-
- Fernandes JK, Day TA, Richardson MS, Sharma AK. Overview of the management of differentiated thyroid cancer. Curr Treat Options Oncol. 2005;6(1):47–57. - PubMed
-
- Solans R, Bosch JA, Galofré P, Porta F, Roselló J, Selva- O'Callagan A, et al. Salivary and lacrimal gland dysfunction (sicca syndrome) after radioiodine therapy. J Nucl Med. 2001;42(5):738–743. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
