Peptide-Directed Binding for the Discovery of Modulators of α-Helix-Mediated Protein-Protein Interactions: Proof-of-Concept Studies with the Apoptosis Regulator Mcl-1
- PMID: 28670766
- PMCID: PMC5577515
- DOI: 10.1002/anie.201705008
Peptide-Directed Binding for the Discovery of Modulators of α-Helix-Mediated Protein-Protein Interactions: Proof-of-Concept Studies with the Apoptosis Regulator Mcl-1
Abstract
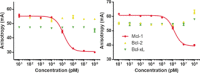
Targeting PPIs with small molecules can be challenging owing to large, hydrophobic binding surfaces. Herein, we describe a strategy that exploits selective α-helical PPIs, transferring these characteristics to small molecules. The proof of concept is demonstrated with the apoptosis regulator Mcl-1, commonly exploited by cancers to avoid cell death. Peptide-directed binding uses few synthetic transformations, requires the production of a small number of compounds, and generates a high percentage of hits. In this example, about 50 % of the small molecules prepared showed an IC50 value of less than 100 μm, and approximately 25 % had IC50 values below 1 μm to Mcl-1. Compounds show selectivity for Mcl-1 over other anti-apoptotic proteins, possess cytotoxicity to cancer cell lines, and induce hallmarks of apoptosis. This approach represents a novel and economic process for the rapid discovery of new α-helical PPI modulators.
Keywords: apoptosis; drug discovery; medicinal chemistry; protein-protein interactions; solid-phase synthesis.
© 2017 The Authors. Published by Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

