Iron Concentration in Deep Gray Matter Structures is Associated with Worse Visual Memory Performance in Healthy Young Adults
- PMID: 28671115
- PMCID: PMC5523837
- DOI: 10.3233/JAD-170118
Iron Concentration in Deep Gray Matter Structures is Associated with Worse Visual Memory Performance in Healthy Young Adults
Abstract
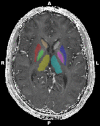
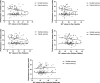
Abnormally high deposition of iron can contribute to neurodegenerative disorders with cognitive impairment. Since previous studies investigating cognition-brain iron accumulation relationships focused on elderly people, our aim was to explore the association between iron concentration in subcortical nuclei and two types of memory performances in a healthy young population. Gender difference was found only in the globus pallidus. Our results showed that iron load characterized by R2* value on the MRI in the caudate and putamen was related to visual memory, while verbal memory was unrelated to iron concentration.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; caudate nucleus; magnetic resonance imaging; memory; putamen; thalamus.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Deep Gray Matter Iron Deposition and Its Relationship to Clinical Features in Cerebral Autosomal Dominant Arteriopathy With Subcortical Infarcts and Leukoencephalopathy Patients: A 7.0-T Magnetic Resonance Imaging Study.Stroke. 2020 Jun;51(6):1750-1757. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.119.028812. Epub 2020 May 13. Stroke. 2020. PMID: 32397933 Clinical Trial.
-
Changes in brain iron concentration after exposure to high-altitude hypoxia measured by quantitative susceptibility mapping.Neuroimage. 2017 Feb 15;147:488-499. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2016.12.033. Epub 2016 Dec 14. Neuroimage. 2017. PMID: 27986608
-
Spatiotemporal variations of magnetic susceptibility in the deep gray matter nuclei from 1 month to 6 years: A quantitative susceptibility mapping study.J Magn Reson Imaging. 2019 Jun;49(6):1600-1609. doi: 10.1002/jmri.26579. Epub 2018 Dec 19. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2019. PMID: 30569483
-
Quantitative susceptibility mapping of brain iron in healthy aging and cognition.Neuroimage. 2023 Nov 15;282:120401. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2023.120401. Epub 2023 Oct 5. Neuroimage. 2023. PMID: 37802405 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The impact of brain iron accumulation on cognition: A systematic review.PLoS One. 2020 Oct 15;15(10):e0240697. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0240697. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 33057378 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Magnetic resonance evidence of increased iron content in subcortical brain regions in asymptomatic Alzheimer's disease.Hum Brain Mapp. 2023 Jun 1;44(8):3072-3083. doi: 10.1002/hbm.26263. Epub 2023 Mar 16. Hum Brain Mapp. 2023. PMID: 36929676 Free PMC article.
-
A positive influence of basal ganglia iron concentration on implicit sequence learning.Brain Struct Funct. 2020 Mar;225(2):735-749. doi: 10.1007/s00429-020-02032-7. Epub 2020 Feb 13. Brain Struct Funct. 2020. PMID: 32055981 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of deep grey nuclei susceptibility in early childhood: a quantitative susceptibility mapping and R2* study at 3 Tesla.Neuroradiology. 2022 May;64(5):1021-1031. doi: 10.1007/s00234-021-02846-0. Epub 2021 Nov 17. Neuroradiology. 2022. PMID: 34787698 Free PMC article.
-
Sex differences in brain iron deposition and microglial ferritin in Alzheimer's disease.Sci Prog. 2025 Apr-Jun;108(2):368504251336080. doi: 10.1177/00368504251336080. Epub 2025 Apr 17. Sci Prog. 2025. PMID: 40247604 Free PMC article.
-
Interscanner reproducibility of volumetric quantitative susceptibility mapping about cerebral subcortical gray nuclei at different MR vendors with the same magnetic strength.Brain Behav. 2024 Apr;14(4):e3473. doi: 10.1002/brb3.3473. Brain Behav. 2024. PMID: 38594225 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hallgren B, Sourander P (1958) The effect of age on the non-haemin iron in the human brain. J Neurochem 3, 41–51. - PubMed
-
- Brass SD, Chen N, Mulkern RV, Bakshi R (2006) Magnetic resonance imaging of iron deposition in neurological disorders. Top Magn Reson Imaging 17, 31–40. - PubMed
-
- Zecca L, Youdim MBH, Riederer P, Connor JR, Crichton RR (2004) Iron, brain ageing and neurodegenerative disorders. Nat Rev Neurosci 5, 863–873. - PubMed
-
- Bartzokis G, Sultzer D, Cummings J, Holt LE, Hance DB, Henderson VW, Mintz J (2000) In vivo evaluation of brain iron in Alzheimer disease using magnetic resonance imaging. Arch Gen Psychiatry 57, 47–53. - PubMed
-
- Bartzokis G (2004) Age-related myelin breakdown: A developmental model of cognitive decline and Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol Aging 25, 5–18. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

