Engineered AAVs for efficient noninvasive gene delivery to the central and peripheral nervous systems
- PMID: 28671695
- PMCID: PMC5529245
- DOI: 10.1038/nn.4593
Engineered AAVs for efficient noninvasive gene delivery to the central and peripheral nervous systems
Abstract
Adeno-associated viruses (AAVs) are commonly used for in vivo gene transfer. Nevertheless, AAVs that provide efficient transduction across specific organs or cell populations are needed. Here, we describe AAV-PHP.eB and AAV-PHP.S, capsids that efficiently transduce the central and peripheral nervous systems, respectively. In the adult mouse, intravenous administration of 1 × 1011 vector genomes (vg) of AAV-PHP.eB transduced 69% of cortical and 55% of striatal neurons, while 1 × 1012 vg of AAV-PHP.S transduced 82% of dorsal root ganglion neurons, as well as cardiac and enteric neurons. The efficiency of these vectors facilitates robust cotransduction and stochastic, multicolor labeling for individual cell morphology studies. To support such efforts, we provide methods for labeling a tunable fraction of cells without compromising color diversity. Furthermore, when used with cell-type-specific promoters and enhancers, these AAVs enable efficient and targetable genetic modification of cells throughout the nervous system of transgenic and non-transgenic animals.
Conflict of interest statement
The California Institute of Technology has filed patent applications related to this work with B.E.D, K.Y.C. and V.G. listed as inventors. B.E.D. and V.G. receive research support from Voyager Therapeutics, which was not used in preparation of this manuscript.
Figures

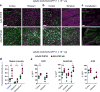


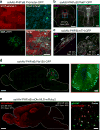
Comment in
-
CREATEd viruses go global.Nat Neurosci. 2017 Jul 26;20(8):1041-1042. doi: 10.1038/nn.4600. Nat Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 28745726 No abstract available.
References
-
- Urban DJ, Roth BL. DREADDs (designer receptors exclusively activated by designer drugs): chemogenetic tools with therapeutic utility. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 2015;55:399–417. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

