Depletion of runt-related transcription factor 2 (RUNX2) enhances SAHA sensitivity of p53-mutated pancreatic cancer cells through the regulation of mutant p53 and TAp63
- PMID: 28671946
- PMCID: PMC5495219
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0179884
Depletion of runt-related transcription factor 2 (RUNX2) enhances SAHA sensitivity of p53-mutated pancreatic cancer cells through the regulation of mutant p53 and TAp63
Abstract
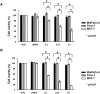
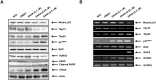
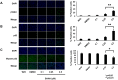
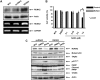
Suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid (SAHA) represents one of the new class of anti-cancer drugs. However, multiple lines of clinical evidence indicate that SAHA might be sometimes ineffective on certain solid tumors including pancreatic cancer. In this study, we have found for the first time that RUNX2/mutant p53/TAp63-regulatory axis has a pivotal role in the determination of SAHA sensitivity of p53-mutated pancreatic cancer MiaPaCa-2 cells. According to our present results, MiaPaCa-2 cells responded poorly to SAHA. Forced depletion of mutant p53 stimulated SAHA-mediated cell death of MiaPaCa-2 cells, which was accomapanied by a further accumulation of γH2AX and cleaved PARP. Under these experimental conditions, pro-oncogenic RUNX2 was strongly down-regulated in mutant p53-depleted MiaPaCa-2 cells. Surprisingly, RUNX2 silencing augmented SAHA-dependent cell death of MiaPaCa-2 cells and caused a significant reduction of mutant p53. Consistent with these observations, overexpression of RUNX2 in MiaPaCa-2 cells restored SAHA-mediated decrease in cell viability and increased the amount of mutant p53. Thus, it is suggestive that there exists a positive auto-regulatory loop between RUNX2 and mutant p53, which might amplify their pro-oncogenic signals. Intriguingly, knockdown of mutant p53 or RUNX2 potentiated SAHA-induced up-regulation of TAp63. Indeed, SAHA-stimulated cell death of MiaPaCa-2 cells was partially attenuated by p63 depletion. Collectively, our present observations strongly suggest that RUNX2/mutant p53/TAp63-regulatory axis is one of the key determinants of SAHA sensitivity of p53-mutated pancreatic cancer cells.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures




Similar articles
-
Depletion of pro-oncogenic RUNX2 enhances gemcitabine (GEM) sensitivity of p53-mutated pancreatic cancer Panc-1 cells through the induction of pro-apoptotic TAp63.Oncotarget. 2016 Nov 1;7(44):71937-71950. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.12433. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27713122 Free PMC article.
-
Improvement of gemcitabine sensitivity of p53-mutated pancreatic cancer MiaPaCa-2 cells by RUNX2 depletion-mediated augmentation of TAp73-dependent cell death.Oncogenesis. 2016 Jun 13;5(6):e233. doi: 10.1038/oncsis.2016.40. Oncogenesis. 2016. PMID: 27294865 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of RUNX2 gene silencing on the gemcitabine sensitivity of p53‑mutated pancreatic cancer MiaPaCa‑2 spheres.Oncol Rep. 2018 Jun;39(6):2749-2758. doi: 10.3892/or.2018.6344. Epub 2018 Mar 30. Oncol Rep. 2018. PMID: 29620279
-
Impact of RUNX2 on drug-resistant human pancreatic cancer cells with p53 mutations.BMC Cancer. 2018 Mar 20;18(1):309. doi: 10.1186/s12885-018-4217-9. BMC Cancer. 2018. PMID: 29558908 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Novel Implications of DNA Damage Response in Drug Resistance of Malignant Cancers Obtained from the Functional Interaction between p53 Family and RUNX2.Biomolecules. 2015 Oct 23;5(4):2854-76. doi: 10.3390/biom5042854. Biomolecules. 2015. PMID: 26512706 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Spatiotemporal switching signals for cancer stem cell activation in pediatric origins of adulthood cancer: Towards a watch-and-wait lifetime strategy for cancer treatment.World J Stem Cells. 2018 Feb 26;10(2):15-22. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v10.i2.15. World J Stem Cells. 2018. PMID: 29531638 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Maitra A, Hruban RH (2008) Pancreatic cancer. Annu Rev Pathol 3: 157–188. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pathmechdis.3.121806.154305 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Le A, Rajeshkumar NV, Maitra A, Dang CV (2012) Conceptual framework for cutting the pancreatic cancer fuel supply. Clin Cancer Res 18: 4285–4290. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-12-0041 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A (2016) Cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin 66: 7–30. doi: 10.3322/caac.21332 - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

