A leprosy clinical severity scale for erythema nodosum leprosum: An international, multicentre validation study of the ENLIST ENL Severity Scale
- PMID: 28671966
- PMCID: PMC5510881
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0005716
A leprosy clinical severity scale for erythema nodosum leprosum: An international, multicentre validation study of the ENLIST ENL Severity Scale
Abstract
Objectives: We wished to validate our recently devised 16-item ENLIST ENL Severity Scale, a clinical tool for measuring the severity of the serious leprosy associated complication of erythema nodosum leprosum (ENL). We also wished to assess the responsiveness of the ENLIST ENL Severity Scale in detecting clinical change in patients with ENL.
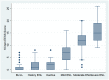
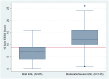
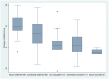
Methods: Participants, recruited from seven centres in six leprosy endemic countries, were assessed using the ENLIST ENL Severity Scale by two researchers, one of whom categorised the severity of ENL. At a subsequent visit a further assessment using the scale was made and both participant and physician rated the change in ENL using the subjective categories of "Much better", "somewhat better", "somewhat worse" and "much worse" compared with "No change" or "about the same".
Results: 447 participants were assessed with the ENLIST ENL Severity Scale. The Cronbach alpha of the scale and each item was calculated to determine the internal consistency of the scale. The ENLIST ENL Severity Scale had good internal consistency and this improved following removal of six items to give a Cronbach's alpha of 0.77. The cut off between mild ENL and more severe disease was 9 determined using ROC curves. The minimal important difference of the scale was determined to be 5 using both participant and physician ratings of change.
Conclusions: The 10-item ENLIST ENL Severity Scale is the first valid, reliable and responsive measure of ENL severity and improves our ability to assess and compare patients and their treatments in this severe and difficult to manage complication of leprosy. The ENLIST ENL Severity Scale will assist physicians in the monitoring and treatment of patients with ENL. The ENLIST ENL Severity Scale is easy to apply and will be useful as an outcome measure in treatment studies and enable the standardisation of other clinical and laboratory ENL research.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures



References
-
- Kumar B, Dogra S, Kaur I. Epidemiological characteristics of leprosy reactions: 15 years experience from north India. Int J Lepr Other Mycobact Dis. 2004;72(2):125–33. doi: 10.1489/1544-581X(2004)072<0125:ECOLRY>2.0.CO;2 . - DOI - PubMed
-
- Pocaterra L, Jain S, Reddy R, Muzaffarullah S, Torres O, Suneetha S, et al. Clinical course of erythema nodosum leprosum: an 11-year cohort study in Hyderabad, India. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2006;74(5):868–79. . - PubMed
-
- Walker SL, Balagon M, Darlong J, Doni SN, Hagge DA, Halwai V, et al. ENLIST 1: An International Multi-centre Cross-sectional Study of the Clinical Features of Erythema Nodosum Leprosum. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2015;9(9):e0004065 doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0004065 . - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Yap FB, Kiung ST, Yap JB. Quality of life in patients with erythema nodosum leprosum in Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia. Indian Dermatol Online J. 2016;7(4):255–8. doi: 10.4103/2229-5178.185495 ; - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Walker SL, Lebas E, Doni SN, Lockwood DN, Lambert SM. The mortality associated with erythema nodosum leprosum in Ethiopia: a retrospective hospital-based study. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2014;8(3):e2690 Epub 2014/03/15. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0002690 ; - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

