The association between Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection and speech and language impairment: A nationwide population-based study in Taiwan
- PMID: 28672017
- PMCID: PMC5495436
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0180402
The association between Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection and speech and language impairment: A nationwide population-based study in Taiwan
Abstract
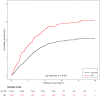
Manifestations of Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection can range from self-limiting upper respiratory symptoms to various neurological complications, including speech and language impairment. But an association between Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection and speech and language impairment has not been sufficiently explored. In this study, we aim to investigate the association between Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection and subsequent speech and language impairment in a nationwide population-based sample using Taiwan's National Health Insurance Research Database. We identified 5,406 children with Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection (International Classification of Disease, Revision 9, Clinical Modification code 4830) and compared to 21,624 age-, sex-, urban- and income-matched controls on subsequent speech and language impairment. The mean follow-up interval for all subjects was 6.44 years (standard deviation = 2.42 years); the mean latency period between the initial Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection and presence of speech and language impairment was 1.96 years (standard deviation = 1.64 years). The results showed that Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection was significantly associated with greater incidence of speech and language impairment [hazard ratio (HR) = 1.49, 95% CI: 1.23-1.80]. In addition, significantly increased hazard ratio of subsequent speech and language impairment in the groups younger than 6 years old and no significant difference in the groups over the age of 6 years were found (HR = 1.43, 95% CI:1.09-1.88 for age 0-3 years group; HR = 1.67, 95% CI: 1.25-2.23 for age 4-5 years group; HR = 1.14, 95% CI: 0.54-2.39 for age 6-7 years group; and HR = 0.83, 95% CI:0.23-2.92 for age 8-18 years group). In conclusion, Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection is temporally associated with incident speech and language impairment.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Association between enterovirus infection and speech and language impairments: A nationwide population-based study.Res Dev Disabil. 2018 Jun;77:76-86. doi: 10.1016/j.ridd.2018.04.017. Epub 2018 Apr 27. Res Dev Disabil. 2018. PMID: 29705533
-
Incident asthma and Mycoplasma pneumoniae: A nationwide cohort study.J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2016 Apr;137(4):1017-1023.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2015.09.032. Epub 2015 Nov 14. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2016. PMID: 26586037
-
Association of Tic Disorders and Enterovirus Infection: A Nationwide Population-Based Study.Medicine (Baltimore). 2016 Apr;95(15):e3347. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000003347. Medicine (Baltimore). 2016. PMID: 27082591 Free PMC article.
-
Infections due to Mycoplasma pneumoniae in childhood.Pediatr Infect Dis. 1986 Jan-Feb;5(1):71-85. doi: 10.1097/00006454-198601000-00014. Pediatr Infect Dis. 1986. PMID: 3080738 Review. No abstract available.
-
Central nervous system manifestations of Mycoplasma pneumoniae infections.J Infect. 2005 Dec;51(5):343-54. doi: 10.1016/j.jinf.2005.07.005. Epub 2005 Sep 19. J Infect. 2005. PMID: 16181677 Review.
Cited by
-
The effect of schistosomiasis and soil-transmitted helminths on expressive language skills among African preschool children.BMC Infect Dis. 2022 Mar 18;22(1):264. doi: 10.1186/s12879-022-07260-2. BMC Infect Dis. 2022. PMID: 35303827 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Foy HM, Kenny GE, McMahan R, Mansy AM, Grayston JT. Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia in an urban area. Five years of surveillance. JAMA. 1970;214(9):1666–72. . - PubMed
-
- Mansel JK, Rosenow EC 3rd, Smith TF, Martin JW Jr. Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia. Chest. 1989;95(3):639–46. . - PubMed
-
- Chaudhry R, Ghosh A, Chandolia A. Pathogenesis of Mycoplasma pneumoniae: An update. Indian J Med Microbiol. 2016;34(1):7–16. doi: 10.4103/0255-0857.174112 . - DOI - PubMed
-
- Tsiodras S, Kelesidis I, Kelesidis T, Stamboulis E, Giamarellou H. Central nervous system manifestations of Mycoplasma pneumoniae infections. J Infect. 2005;51(5):343–54. doi: 10.1016/j.jinf.2005.07.005 . - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical