Repositioning Bazedoxifene as a novel IL-6/GP130 signaling antagonist for human rhabdomyosarcoma therapy
- PMID: 28672024
- PMCID: PMC5495564
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0180297
Repositioning Bazedoxifene as a novel IL-6/GP130 signaling antagonist for human rhabdomyosarcoma therapy
Abstract
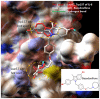
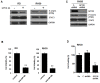
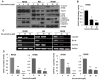
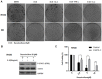
Interleukins-6 (IL-6)/GP130 signaling pathway represents a promising target for cancer therapy due to its critical role in survival and progression of multiple types of cancer. We have identified Bazedoxifene, a Food and Drug Administration (FDA)-approved drug used for the prevention of postmenopausal osteoporosis, with novel function as inhibitor of IL-6/GP130 interaction. In this study, we investigate the effect of Bazedoxifene in rhabdomyosarcoma and evaluate whether inhibiting IL-6/GP130 signaling is an effective therapeutic strategy for rhabdomyosarcoma. The inhibitory effect of Bazedoxifene was assessed in rhabdomyosarcoma cell lines in vitro and RH30 xenograft model was used to further examine the suppressive efficacy of Bazedoxifene on tumor growth in vivo. Rhabdomyosarcoma cells showed their sensitivity to GP130 inhibition using gene knockdown or neutralized antibody, suggesting IL-6/GP130 as therapeutic target in rhabdomyosarcoma cells. Bazedoxifene decreased the signal transducer and activator of transcription3 (STAT3) phosphorylation, blocked STAT3 DNA binding, and down-regulated the expression of STAT3 downstream genes. Bazedoxifene also induced cell apoptosis, reduced cell viability, and inhibited colony formation in rhabdomyosarcoma cells. The inhibition of colony formation, STAT3 phosphorylation, or cell viability following Bazedoxifene treatment was partially reversed by addition of excess IL-6 or overexpression of constitutive STAT3, respectively, supporting Bazedoxifene acted through IL-6/GP130 signaling. In addition, Bazedoxifene repressed cell invasion and angiogenesis in vitro. Furthermore, oral administration of Bazedoxifene significantly suppressed tumor growth and expression of STAT3 phosphorylation in nude mice bearing established human rhabdomyosarcoma xenograft. Taken together, these findings validate IL-6/GP130 signaling as therapeutic target in rhabdomyosarcoma and provide first evidence that Bazedoxifene may serve as a novel promising drug targeting IL-6/GP130 for treatment of rhabdomyosarcoma.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Bazedoxifene is a novel IL-6/GP130 inhibitor for treating triple-negative breast cancer.Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2019 Jun;175(3):553-566. doi: 10.1007/s10549-019-05183-2. Epub 2019 Mar 9. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2019. PMID: 30852762
-
Bazedoxifene as a novel GP130 inhibitor for Colon Cancer therapy.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2019 Feb 8;38(1):63. doi: 10.1186/s13046-019-1072-8. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2019. PMID: 30736824 Free PMC article.
-
Bazedoxifene as a Novel GP130 Inhibitor for Pancreatic Cancer Therapy.Mol Cancer Ther. 2016 Nov;15(11):2609-2619. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-15-0921. Epub 2016 Aug 17. Mol Cancer Ther. 2016. PMID: 27535971 Free PMC article.
-
Bazedoxifene as a Potential Cancer Therapeutic Agent Targeting IL-6/GP130 Signaling.Curr Oncol. 2024 Sep 25;31(10):5737-5751. doi: 10.3390/curroncol31100426. Curr Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39451730 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Therapeutic strategies for targeting the IL-6/STAT3 cytokine signaling pathway in inflammatory bowel disease.Anticancer Res. 2007 Nov-Dec;27(6A):3749-56. Anticancer Res. 2007. PMID: 17970038 Review.
Cited by
-
Ectopic CD137 expression by rhabdomyosarcoma provides selection advantages but allows immunotherapeutic targeting.Oncoimmunology. 2021 Feb 4;10(1):1877459. doi: 10.1080/2162402X.2021.1877459. Oncoimmunology. 2021. PMID: 33643694 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting the gp130/STAT3 Axis Attenuates Tumor Microenvironment Mediated Chemoresistance in Group 3 Medulloblastoma Cells.Cells. 2022 Jan 23;11(3):381. doi: 10.3390/cells11030381. Cells. 2022. PMID: 35159191 Free PMC article.
-
Bazedoxifene as a novel strategy for treatment of pancreatic and gastric adenocarcinoma.Oncotarget. 2019 May 7;10(34):3198-3202. eCollection 2019 May 7. Oncotarget. 2019. PMID: 31139333 Free PMC article.
-
Synergistic effect of bazedoxifene and abemaciclib co‑treatment in triple‑negative breast cancer cells in vitro.Oncol Lett. 2024 Sep 19;28(6):554. doi: 10.3892/ol.2024.14688. eCollection 2024 Dec. Oncol Lett. 2024. PMID: 39355786 Free PMC article.
-
Bazedoxifene, a GP130 Inhibitor, Modulates EMT Signaling and Exhibits Antitumor Effects in HPV-Positive Cervical Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Aug 13;22(16):8693. doi: 10.3390/ijms22168693. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34445405 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Pappo A. Rhabdomyosarcoma and other soft tissue sarcomas in children. Curr Opin Oncol 1996;8:311–6. - PubMed
-
- Siegel DA, King J, Tai E, Buchanan N, Ajani UA, Li J. Cancer incidence rates and trends among children and adolescents in the United States, 2001–2009. Pediatrics. 2014;134(4):e945–55. Epub 2014/09/10. doi: 10.1542/peds.2013-3926 ; - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Egas-Bejar D, Huh WW. Rhabdomyosarcoma in adolescent and young adult patients: current perspectives. Adolescent health, medicine and therapeutics. 2014;5:115–25. Epub 2014/06/27. doi: 10.2147/AHMT.S44582 ; - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Arndt CA, Rose PS, Folpe AL, Laack NN. Common musculoskeletal tumors of childhood and adolescence. Mayo Clinic proceedings. 2012;87(5):475–87. Epub 2012/05/09. doi: 10.1016/j.mayocp.2012.01.015 ; - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kishimoto T. Signal transduction through homo- or heterodimers of gp130. Stem Cells. 1994;1:37–44. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

