Comprehensive identification of age-related lipidome changes in rat amygdala during normal aging
- PMID: 28672041
- PMCID: PMC5495493
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0180675
Comprehensive identification of age-related lipidome changes in rat amygdala during normal aging
Abstract
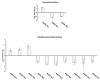
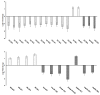
Brain lipids are integral components of brain structure and function. However, only recent advancements of chromatographic techniques together with mass spectrometry allow comprehensive identification of lipid species in complex brain tissue. Lipid composition varies between the individual areas and the majority of previous reports was focusing on individual lipids rather than a lipidome. Herein, a mass spectrometry-based approach was used to evaluate age-related changes in the lipidome of the rat amygdala obtained from young (3 months) and old (20 months) males of the Sprague-Dawley rat strain. A total number of 70 lipid species with significantly changed levels between the two animal groups were identified spanning four main lipid classes, i.e. glycerolipids, glycerophospholipids, sphingolipids and sterol lipids. These included phospholipids with pleiotropic brain function, such as derivatives of phosphatidylcholine, phosphatidylserine, and phosphatidylethanolamine. The analysis also revealed significant level changes of phosphatidic acid, diacylglycerol, sphingomyelin and ceramide that directly represent lipid signaling and affect amygdala neuronal activity. The amygdala is a crucial brain region for cognitive functions and former studies on rats and humans showed that this region changes its activity during normal aging. As the information on amygdala lipidome is very limited the results obtained in the present study represent a significant novelty and may contribute to further studies on the role of lipid molecules in age-associated changes of amygdala function.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Piomelli D, Astarita G, Rapaka R. A neuroscientist's guide to lipidomics. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2007;8(10):743–54. doi: 10.1038/nrn2233 . - DOI - PubMed
-
- Muller CP, Reichel M, Muhle C, Rhein C, Gulbins E, Kornhuber J. Brain membrane lipids in major depression and anxiety disorders. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015;1851(8):1052–65. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2014.12.014 . - DOI - PubMed
-
- Wenk MR. The emerging field of lipidomics. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2005;4(7):594–610. doi: 10.1038/nrd1776 . - DOI - PubMed
-
- Dawson G. Measuring brain lipids. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015;1851(8):1026–39. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2015.02.007 ; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC4457555. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Brugger B. Lipidomics: analysis of the lipid composition of cells and subcellular organelles by electrospray ionization mass spectrometry. Annu Rev Biochem. 2014;83:79–98. doi: 10.1146/annurev-biochem-060713-035324 . - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

