Augmented Anticancer Effects of Cantharidin with Liposomal Encapsulation: In Vitro and In Vivo Evaluation
- PMID: 28672816
- PMCID: PMC6152072
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules22071052
Augmented Anticancer Effects of Cantharidin with Liposomal Encapsulation: In Vitro and In Vivo Evaluation
Abstract
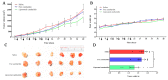
PEGylated liposomes have received much attention as pharmaceutical carriers to deliver chemotherapeutic agents for therapeutic purpose. The aim of this study was to prepare and characterize PEGylated liposome of cantharidin and investigate its therapeutic effect on human hepatocellular carcinoma treatment in vitro and in vivo. Liposomal cantharidin was evaluated for their anticancer effects in vitro using human hepatocellular carcinoma HepG2 cells and in vivo using HepG2-bearing nude mice compared to free drug. PEGylated liposome of cantharidin had a particle size of 129.9 nm and a high encapsulation efficacy of approximately 88.9%. The liposomal cantharidin had a higher anti-proliferative effect vis-à-vis free cantharidin in inducing G2/M cell cycle arrest and apoptosis. Liposomal cantharidin killed more HepG2 cancer cells at the same concentration equivalent to free cantharidin. Further study in vivo also showed that liposomal cantharidin achieved a higher tumor growth inhibition efficacy than free drug on hepatocellular carcinoma. As our study exhibited enhanced cytotoxicity against HepG2 cells and augmented tumor inhibitory effects in vivo, the results validate the potential value of cantharidin-liposome in improving the therapeutic efficacy of cantharidin for liver cancer.
Keywords: HepG2; PEGylated liposome; anti-proliferative effect; cantharidin; drug delivery system; hepatocellular carcinoma; xenograft tumor.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Dual-Functional Liposomes with Carbonic Anhydrase IX Antibody and BR2 Peptide Modification Effectively Improve Intracellular Delivery of Cantharidin to Treat Orthotopic Hepatocellular Carcinoma Mice.Molecules. 2019 Sep 12;24(18):3332. doi: 10.3390/molecules24183332. Molecules. 2019. PMID: 31547459 Free PMC article.
-
Liposome encapsulation reduces cantharidin toxicity.Food Chem Toxicol. 2008 Sep;46(9):3116-21. doi: 10.1016/j.fct.2008.06.084. Epub 2008 Jul 4. Food Chem Toxicol. 2008. PMID: 18652872
-
Cantharidin inhibits cell proliferation and induces apoptosis through G2/M phase cell cycle arrest in hepatocellular carcinoma stem cells.Oncol Rep. 2016 May;35(5):2970-6. doi: 10.3892/or.2016.4684. Epub 2016 Mar 17. Oncol Rep. 2016. PMID: 26986084
-
Exploring Cantharidin and its Analogues as Anticancer Agents: A Review.Curr Med Chem. 2023;30(18):2006-2019. doi: 10.2174/0929867330666221103151537. Curr Med Chem. 2023. PMID: 36330637 Review.
-
Antitumor potential of the protein phosphatase inhibitor, cantharidin, and selected derivatives.Bioorg Med Chem. 2021 Feb 15;32:116012. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2021.116012. Epub 2021 Jan 9. Bioorg Med Chem. 2021. PMID: 33454654 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Lipid based nanoparticles as a novel treatment modality for hepatocellular carcinoma: a comprehensive review on targeting and recent advances.J Nanobiotechnology. 2022 Mar 5;20(1):109. doi: 10.1186/s12951-022-01309-9. J Nanobiotechnology. 2022. PMID: 35248080 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Development of 11-DGA-3-O-Gal-Modified Cantharidin Liposomes for Treatment of Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Molecules. 2019 Aug 24;24(17):3080. doi: 10.3390/molecules24173080. Molecules. 2019. PMID: 31450608 Free PMC article.
-
Lipid-Based Nanoparticles: Application and Recent Advances in Cancer Treatment.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2019 Apr 19;9(4):638. doi: 10.3390/nano9040638. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31010180 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lipid-Based Nanoparticles as a Pivotal Delivery Approach in Triple Negative Breast Cancer (TNBC) Therapy.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Sep 3;23(17):10068. doi: 10.3390/ijms231710068. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36077466 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dual-Functional Liposomes with Carbonic Anhydrase IX Antibody and BR2 Peptide Modification Effectively Improve Intracellular Delivery of Cantharidin to Treat Orthotopic Hepatocellular Carcinoma Mice.Molecules. 2019 Sep 12;24(18):3332. doi: 10.3390/molecules24183332. Molecules. 2019. PMID: 31547459 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

