Volunteer navigation partnerships: Piloting a compassionate community approach to early palliative care
- PMID: 28673300
- PMCID: PMC5496423
- DOI: 10.1186/s12904-017-0210-3
Volunteer navigation partnerships: Piloting a compassionate community approach to early palliative care
Erratum in
-
Erratum to: BMC Palliative Care, Vol. 17.BMC Palliat Care. 2017 Oct 10;16(1):51. doi: 10.1186/s12904-017-0233-9. BMC Palliat Care. 2017. PMID: 29017489 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Background: A compassionate community approach to palliative care provides important rationale for building community-based hospice volunteer capacity. In this project, we piloted one such capacity-building model in which volunteers and a nurse partnered to provide navigation support beginning in the early palliative phase for adults living in community. The goal was to improve quality of life by developing independence, engagement, and community connections.
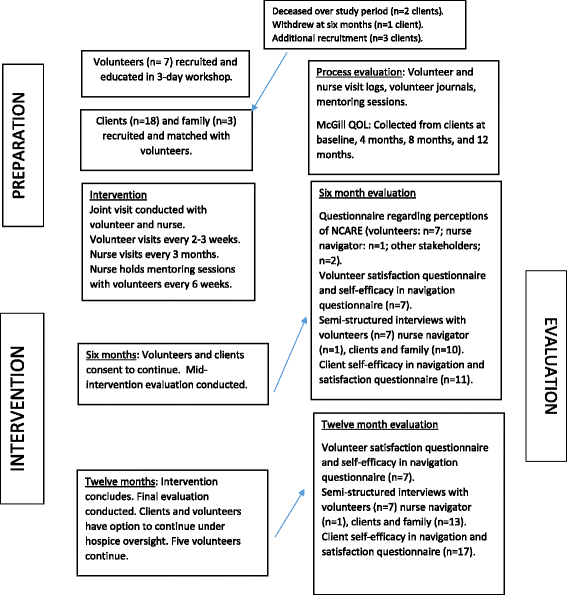
Methods: Volunteers received navigation training through a three-day workshop and then conducted in-home visits with clients living with advanced chronic illness over one year. A nurse navigator provided education and mentorship. Mixed method evaluation data was collected from clients, volunteer navigators, the nurse navigator, and other stakeholders.
Results: Seven volunteers were partnered with 18 clients. Over the one-year pilot, the volunteer navigators conducted visits in home or by phone every two to three weeks. Volunteers were skilled and resourceful in building connections and facilitating engagement. Although it took time to learn the navigator role, volunteers felt well-prepared and found the role satisfying and meaningful. Clients and family rated the service as highly important to their care because of how the volunteer helped to make the difficult experiences of aging and advanced chronic illness more livable. Significant benefits cited by clients were making good decisions for both now and in the future; having a surrogate social safety net; supporting engagement with life; and ultimately, transforming the experience of living with illness. Overall the program was perceived to be well-designed by stakeholders and meeting an important need in the community. Sustainability, however, was a concern expressed by both clients and volunteers.
Conclusions: Volunteers providing supportive navigation services during the early phase of palliative care is a feasible way to foster a compassionate community approach to care for an aging population. The program is now being implemented by hospice societies in diverse communities across Canada.
Keywords: Compassionate community; Hospice and palliative care; Navigation; Public health; Volunteers.
References
-
- McKee M, Kelley ML, Guirguis-Younger M. So no one dies alone: a study of hospice volunteering with rural seniors. J Palliat Care. 2007;23:163–172. - PubMed
-
- McKee M, Kelley ML, Guirguis-Younger M, MacLean M, Nadin S. It takes a whole community: the contribution of rural hospice volunteers to whole-person palliative care. J Palliat Care. 2010;26:103–111. - PubMed
-
- Duggleby WD, Penz K, Leipert BD, Wilson DM, Goodridge D, Williams A. ‘I am part of the community but...’ The changing context of rural living for persons with advanced cancer and their families. Rural Remote Health. 2011;11:1–12. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical