Mechanisms of Resistance to ABL Kinase Inhibition in Chronic Myeloid Leukemia and the Development of Next Generation ABL Kinase Inhibitors
- PMID: 28673390
- PMCID: PMC5505321
- DOI: 10.1016/j.hoc.2017.04.007
Mechanisms of Resistance to ABL Kinase Inhibition in Chronic Myeloid Leukemia and the Development of Next Generation ABL Kinase Inhibitors
Abstract
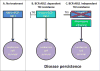
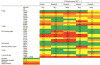
Chronic myeloid leukemia is increasingly viewed as a chronic illness; most patients have a life expectancy close to that of the general population. Despite progress made using BCR-ABL1 tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs), drug resistance via BCR-ABL1-dependent and BCR-ABL1-independent mechanisms continues to be an issue. BCR-ABL1-dependent resistance is primarily mediated through oncoprotein kinase domain mutations and usually results in overt resistance to TKIs. However, BCR-ABL1-independent resistance in the setting of effective BCR-ABL1 inhibition is recognized as a major contributor to minimal residual disease. Efforts to eradicate persistent leukemic stem cells have focused on combination therapy.
Keywords: BCR-ABL1; Chronic myeloid leukemia (CML); Drug resistance; Mutation; Treatment-free remission (TFR); Tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI).
Published by Elsevier Inc.
Figures


References
-
- SEER Cancer Statistics Factsheets: Chronic Myeloid Leukemia. National Cancer Institute; Bethesda, MD: http://seer.cancer.gov/statfacts/html/cmyl.html.
-
- Ren R. Mechanisms of BCR-ABL in the pathogenesis of chronic myelogenous leukaemia. Nat Rev Cancer. 2005;5:172–83. - PubMed
-
- Bower H, Bjorkholm M, Dickman PW, et al. Life Expectancy of Patients With Chronic Myeloid Leukemia Approaches the Life Expectancy of the General Population. J Clin Oncol. 2016;34:2851–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

