PKA-mediated Gli2 and Gli3 phosphorylation is inhibited by Hedgehog signaling in cilia and reduced in Talpid3 mutant
- PMID: 28673820
- PMCID: PMC5831674
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2017.06.035
PKA-mediated Gli2 and Gli3 phosphorylation is inhibited by Hedgehog signaling in cilia and reduced in Talpid3 mutant
Abstract
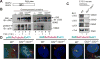
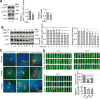
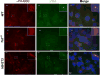
Hedgehog (Hh) signaling is thought to occur in primary cilia, but the molecular basis of Gli2 and Gli3 activation by Hh signaling in cilia is unknown. Similarly, how ciliary gene mutations result in reduced Gli3 processing that generates a repressor is also not clear. Here we show that Hh signaling inhibits Gli2 and Gli3 phosphorylation by protein kinase A (PKA) in cilia. The cilia related gene Talpid3 (Ta3) mutation results in the reduced processing and phosphorylation of Gli2 and Gli3. Interestingly, Ta3 interacts and colocalizes with PKA regulatory subunit PKARIIβ at centrioles in the cell. The centriolar localization and PKA binding regions are located in the N- and C-terminal regions of Ta3, respectively. PKARIIβ fails to localize at centrioles in some Ta3 mutant cells. Therefore, our study provides the direct evidence that Gli2 and Gli3 are dephosphorylated and activated in cilia and that impaired Gli2 and Gli3 processing in Ta3 mutant is at least in part due to a decrease in Gli2 and Gli3 phosphorylation.
Keywords: Cilia; Gli2; Gli3; Hedgehog; PKA; Talpid3.
Copyright © 2017 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
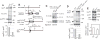


References
-
- Bai CB, Stephen D, Joyner AL. All mouse ventral spinal cord patterning by hedgehog is Gli dependent and involves an activator function of Gli3. Dev. Cell. 2004;6:103–115. - PubMed
-
- Briscoe J, Pierani A, Jessell TM, Ericson J. A homeodomain protein code specifies progenitor cell identity and neuronal fate in the ventral neural tube. Cell. 2000;101:435–445. - PubMed
-
- Caspary T, Larkins CE, Anderson KV. The graded response to Sonic Hedgehog depends on cilia architecture. Dev. Cell. 2007;12:767–778. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

