Elucidating reaction mechanisms on quantum computers
- PMID: 28674011
- PMCID: PMC5530650
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1619152114
Elucidating reaction mechanisms on quantum computers
Abstract
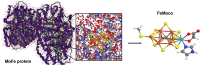
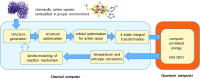
With rapid recent advances in quantum technology, we are close to the threshold of quantum devices whose computational powers can exceed those of classical supercomputers. Here, we show that a quantum computer can be used to elucidate reaction mechanisms in complex chemical systems, using the open problem of biological nitrogen fixation in nitrogenase as an example. We discuss how quantum computers can augment classical computer simulations used to probe these reaction mechanisms, to significantly increase their accuracy and enable hitherto intractable simulations. Our resource estimates show that, even when taking into account the substantial overhead of quantum error correction, and the need to compile into discrete gate sets, the necessary computations can be performed in reasonable time on small quantum computers. Our results demonstrate that quantum computers will be able to tackle important problems in chemistry without requiring exorbitant resources.
Keywords: quantum algorithms; quantum computing; reaction mechanisms.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Dykstra C, Frenking G, Kim KS, Scuseria GE. Theory and Applications of Computational Chemistry: The First Forty Years. Elsevier; Amsterdam: 2005.
-
- Cramer CJ, Truhlar DG. Density functional theory for transition metals and transition metal chemistry. Phys Chem Chem Phys. 2009;11:10757–10816. - PubMed
-
- Jiang W, DeYonker NJ, Determan JJ, Wilson AK. Toward accurate theoretical thermochemistry of first row transition metal complexes. J Phys Chem A. 2012;116:870–885. - PubMed
-
- Weymuth T, Couzijn EPA, Chen P, Reiher M. New benchmark set of transition-metal coordination reactions for the assessment of density functionals. J Chem Theor Comput. 2014;10:3092–3103. - PubMed
-
- Lloyd S. Universal quantum simulators. Science. 1996;273:1073–1078. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

