Prevalence of and Risk Factors for Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy in Youth With Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes: SEARCH for Diabetes in Youth Study
- PMID: 28674076
- PMCID: PMC5566278
- DOI: 10.2337/dc17-0179
Prevalence of and Risk Factors for Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy in Youth With Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes: SEARCH for Diabetes in Youth Study
Abstract
Objective: We assessed the prevalence of and risk factors for diabetic peripheral neuropathy (DPN) in youth with type 1 diabetes (T1D) and type 2 diabetes (T2D) enrolled in the SEARCH for Diabetes in Youth (SEARCH) study.
Research design and methods: The Michigan Neuropathy Screening Instrument (MNSI) was used to assess DPN in 1,734 youth with T1D (mean ± SD age 18 ± 4 years, T1D duration 7.2 ± 1.2 years, and HbA1c 9.1 ± 1.9%) and 258 youth with T2D (age 22 ± 3.5 years, T2D duration 7.9 ± 2 years, and HbA1c 9.4 ± 2.3%) who were enrolled in the SEARCH study and had ≥5 years of diabetes duration. DPN was defined as an MNSI exam score of >2. Glycemic control over time was estimated as area under the curve for HbA1c.
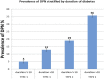
Results: The prevalence of DPN was 7% in youth with T1D and 22% in youth with T2D. Risk factors for DPN in youth with T1D were older age, longer diabetes duration, smoking, increased diastolic blood pressure, obesity, increased LDL cholesterol and triglycerides, and lower HDL cholesterol (HDL-c). In youth with T2D, risk factors were older age, male sex, longer diabetes duration, smoking, and lower HDL-c. Glycemic control over time was worse among those with DPN compared with those without for youth with T1D (odds ratio 1.53 [95% CI 1.24; 1.88]) but not for youth with T2D (1.05 [0.7; 1.56]).
Conclusions: The high rates of DPN among youth with diabetes are a cause of concern and suggest a need for early screening and better risk factor management. Interventions in youth that address poor glycemic control and dyslipidemia may prevent or delay debilitating neuropathic complications.
© 2017 by the American Diabetes Association.
Figures
Comment in
-
Comment on Jaiswal et al. Prevalence of and Risk Factors for Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy in Youth With Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes: SEARCH for Diabetes in Youth Study. Diabetes Care 2017;40:1226-1232.Diabetes Care. 2018 Mar;41(3):e35-e36. doi: 10.2337/dc17-2175. Diabetes Care. 2018. PMID: 29463673 No abstract available.
-
Response to Comment on Jaiswal et al. Prevalence of and Risk Factors for Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy in Youth With Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes: SEARCH for Diabetes in Youth Study. Diabetes Care 2017;40:1226-1232.Diabetes Care. 2018 Mar;41(3):e37. doi: 10.2337/dci17-0058. Diabetes Care. 2018. PMID: 29463674 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Bao XH, Wong V, Wang Q, Low LC. Prevalence of peripheral neuropathy with insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Pediatr Neurol 1999;20:204–209 - PubMed
-
- Nordwall M, Hyllienmark L, Ludvigsson J. Early diabetic complications in a population of young patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus despite intensive treatment. J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab 2006;19:45–54 - PubMed
-
- Blankenburg M, Kraemer N, Hirschfeld G, et al. Childhood diabetic neuropathy: functional impairment and non-invasive screening assessment. Diabet Med 2012;29:1425–1432 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- P30 DK057516/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UC4 DK108173/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U18 DP002710/DP/NCCDPHP CDC HHS/United States
- U18 DP006134/DP/NCCDPHP CDC HHS/United States
- U18DP006138/ACL/ACL HHS/United States
- U18 DP002714/DP/NCCDPHP CDC HHS/United States
- U01 DP000248/DP/NCCDPHP CDC HHS/United States
- U18DP006133/ACL/ACL HHS/United States
- U01 DP000244/DP/NCCDPHP CDC HHS/United States
- U18DP006131/ACL/ACL HHS/United States
- U18 DP002709/DP/NCCDPHP CDC HHS/United States
- P30 DK020572/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U18 DP002708/DP/NCCDPHP CDC HHS/United States
- U01 DP000247/DP/NCCDPHP CDC HHS/United States
- U18DP006136/ACL/ACL HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000154/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- U18DP006134/ACL/ACL HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001425/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR002319/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK127208/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000423/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- EP-C-15-002/EPA/EPA/United States
- U01 DP000250/DP/NCCDPHP CDC HHS/United States
- U18DP006139/ACL/ACL HHS/United States
- U01 DP000246/DP/NCCDPHP CDC HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001450/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DP000254/DP/NCCDPHP CDC HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous