Identification of Novel Associations of Candidate Genes with Resistance to Late Blight in Solanum tuberosum Group Phureja
- PMID: 28674545
- PMCID: PMC5475386
- DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2017.01040
Identification of Novel Associations of Candidate Genes with Resistance to Late Blight in Solanum tuberosum Group Phureja
Abstract
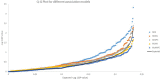
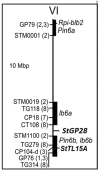
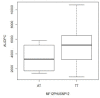
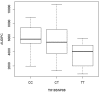
The genetic basis of quantitative disease resistance has been studied in crops for several decades as an alternative to R gene mediated resistance. The most important disease in the potato crop is late blight, caused by the oomycete Phytophthora infestans. Quantitative disease resistance (QDR), as any other quantitative trait in plants, can be genetically mapped to understand the genetic architecture. Association mapping using DNA-based markers has been implemented in many crops to dissect quantitative traits. We used an association mapping approach with candidate genes to identify the first genes associated with quantitative resistance to late blight in Solanum tuberosum Group Phureja. Twenty-nine candidate genes were selected from a set of genes that were differentially expressed during the resistance response to late blight in tetraploid European potato cultivars. The 29 genes were amplified and sequenced in 104 accessions of S. tuberosum Group Phureja from Latin America. We identified 238 SNPs in the selected genes and tested them for association with resistance to late blight. The phenotypic data were obtained under field conditions by determining the area under disease progress curve (AUDPC) in two seasons and in two locations. Two genes were associated with QDR to late blight, a potato homolog of thylakoid lumen 15 kDa protein (StTL15A) and a stem 28 kDa glycoprotein (StGP28). Key message: A first association mapping experiment was conducted in Solanum tuberosum Group Phureja germplasm, which identified among 29 candidates two genes associated with quantitative resistance to late blight.
Keywords: SNP; association mapping; candidate genes; late blight; quantitative disease resistance.
Figures
References
-
- Álvarez M. F., Mosquera T., Blair M. W. (2015). The use of association genetics approaches in plant breeding. Plant Breed. Rev. 38 Chap. 2 17–67.
-
- Bormann C. A., Rickert A. M., Castillo R. A., Paal J., Lübeck J., Strahwald J., et al. (2004). Tagging quantitative trait loci for maturity-corrected late blight resistance in tetraploid potato with PCR-based candidate gene markers. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 17 1126–1138. 10.1094/MPMI.2004.17.10.1126 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

