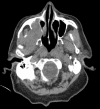
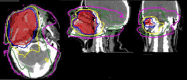
[Ameloblastoma of the maxillary sinus treated with radiation therapy]
- PMID: 28674562
- PMCID: PMC5483349
- DOI: 10.11604/pamj.2017.26.169.8992
[Ameloblastoma of the maxillary sinus treated with radiation therapy]
Abstract
Ameloblastoma is a benign aggressive odontogenic tumor which requires early diagnosis and appropriate treatment. It commonly affects the mandible and radical surgery is the gold standard treatment. We report the case of a patient with ameloblastoma in extremely advanced phase affecting the maxillary sinus who was treated with intensity modulated conformal radiation therapy. Patient's evolution was marked by complete remission maintained after 24 months follow-up. Maxillary ameloblastoma is not well documented in the literature. It is usually diagnosed at the later stage when optimal surgery cannot be performed. This case study aimed to demonstrate that radiation therapy is a real therapeutic alternative in the treatment of advanced and inoperable forms of ameloblastoma.
L’améloblastome est une tumeur odontogène bénigne à caractère agressif qui nécessite un diagnostic précoce et un traitement adéquat. Son site habituel est la mandibule et la chirurgie radicale demeure le traitement de référence. Nous rapportons le cas d’un améloblastome à localisation sinusienne maxillaire localement très avancé que nous avons traité par radiothérapie conformationnelle avec modulation d’intensité. L’évolution a été marquée par une rémission de la maladie avec un recul de 24 mois. La localisation maxillaire d’un améloblastome est rarement décrite, diagnostiquée à un stade tardif le plus souvent où la chirurgie optimale est impossible. A travers cette observation nous démontrons que la radiothérapie constitue une véritable alternative thérapeutique dans les formes évoluées et inopérables des améloblastomes.
Keywords: Ameloblastoma; maxillary; tumor.
Conflict of interest statement
Les auteurs ne déclarent aucun conflit d'interêts.
Figures
References
-
- Canon RC. Clinical and Pathologic Diagnosis: Pathology quiz case. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 1986;112:890–2. - PubMed
-
- Mendenhall WM, Werning JW, Fernandes R, Malyapa RS, Mendenhal NP. Ameloblastoma. Am J Clin Oncol. 2007 Dec;30(6):645–8. - PubMed
-
- Dunfee BL, Sakai O, Pistey R, Gohel A. Radiologic and pathologic characteristics of benign and malignant lesions of the mandible. Radiographics. 2006 Nov-Dec;26(6):1751–68. - PubMed
-
- Vallicioni J, Loum BB, Dassonville O, Poissonnet G, Ettore F, Demard F. Les améloblastomes. Annales d'Otolaryngologie et de Chirurgie Cervico-faciale. 2007 Sep;124(4):166–171. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources