Primary structure and expression of a functional human glucocorticoid receptor cDNA
- PMID: 2867473
- PMCID: PMC6165583
- DOI: 10.1038/318635a0
Primary structure and expression of a functional human glucocorticoid receptor cDNA
Abstract
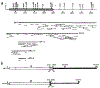
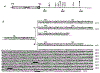
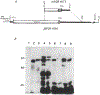
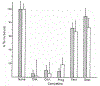
Identification of complementary DNAs encoding the human glucocorticoid receptor predicts two protein forms, of 777 (alpha) and 742 (beta) amino acids, which differ at their carboxy termini. The proteins contain a cysteine/lysine/arginine-rich region which may define the DNA-binding domain. Pure radiolabelled glucocorticoid receptor, synthesized in vitro, is immunoreactive and possesses intrinsic steroid-binding activity characteristic of the native glucocorticoid receptor.
Figures


References
-
- Jensen EV & De Sombre ER A. Rev. Biochem 41, 203–230 (1972). - PubMed
-
- Gorski J & Gannon FA, Rev. Physiol 38, 425–450 (1976). - PubMed
-
- Yamamoto K,R & Alberts BM A. Rev. Biochem 45, 721–746 (1976). - PubMed
-
- O’Malley BW, McGuire WL, Kohler PO & Komtman SG Recent Prog. Horm. Res 25, 105–160 (1969). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

