Diabetic rats present higher urinary loss of proteins and lower renal expression of megalin, cubilin, ClC-5, and CFTR
- PMID: 28676554
- PMCID: PMC5506523
- DOI: 10.14814/phy2.13335
Diabetic rats present higher urinary loss of proteins and lower renal expression of megalin, cubilin, ClC-5, and CFTR
Abstract
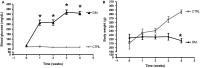
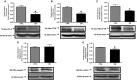
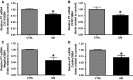
Diabetic nephropathy (DN) occurs in around 40% of those with diabetes. Proteinuria is the main characteristic of DN and develops as a result of increased permeability of the glomerulus capillary wall and/or decreased proximal tubule endocytosis. The goal of this work was to evaluate renal function and the expression of megalin, cubilin, CFTR (cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator), and ClC-5 in the proximal tubule and renal cortex of rats with type 1 diabetes. Male Wistar rats were randomly assigned to control (CTRL) and diabetic (DM) groups for 4 weeks. Renal function was assessed in 24-h urine sample by calculating clearance and fractional excretion of solutes. The RNA and protein contents of ClC-5, CFTR, megalin, and cubilin were determined in the renal proximal tubule and cortex using real-time polymerase chain reaction and western blotting techniques, respectively. The results showed higher creatinine clearance and higher urinary excretion of proteins, albumin, and transferrin in the DM group than in the CTRL group. Furthermore, the renal cortex and proximal tubule of diabetic animals showed downregulation of megalin, cubilin, ClC-5, and CFTR, critical components of the endocytic apparatus. These data suggest dysfunction in proximal tubule low-molecular-weight endocytosis and protein glomerulus filtration in the kidney of diabetic rats.
Keywords: CFTR; ClC‐5; cubilin; diabetes; endocytosis; kidney; megalin; proximal tubule.
© 2017 The Authors. Physiological Reports published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc. on behalf of The Physiological Society and the American Physiological Society.
Figures


References
-
- Alberti, K. G. , and Zimmet P. Z.. 1998. Definition, diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus and its complications. Part 1: diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus provisional report of a WHO consultation. Diabet. Med. 15:539–553. - PubMed
-
- Bardoux, P. , Ahloulay M., Le Maout S., Bankir L., and Trinh‐Trang‐Tan M. M.. 2001. Aquaporin‐2 and urea transporter‐A1 are up‐regulated in rats with type I diabetes mellitus. Diabetologia 44:637–645. - PubMed
-
- Barth, J. L. , and Argraves W. S.. 2001. Cubilin and megalin: partners in lipoprotein and vitamin metabolism. Trends Cardiovasc. Med. 11:26–31. - PubMed
-
- Betz, B. , and Conway B. R.. 2014. Recent advances in animal models of diabetic nephropathy. Nephron. Exp. Nephrol. 126:191–195. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

