Yellow Rust Epidemics Worldwide Were Caused by Pathogen Races from Divergent Genetic Lineages
- PMID: 28676811
- PMCID: PMC5477562
- DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2017.01057
Yellow Rust Epidemics Worldwide Were Caused by Pathogen Races from Divergent Genetic Lineages
Abstract
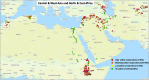
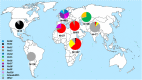
We investigated whether the recent worldwide epidemics of wheat yellow rust were driven by races of few clonal lineage(s) or populations of divergent races. Race phenotyping of 887 genetically diverse Puccinia striiformis isolates sampled in 35 countries during 2009-2015 revealed that these epidemics were often driven by races from few but highly divergent genetic lineages. PstS1 was predominant in North America; PstS2 in West Asia and North Africa; and both PstS1 and PstS2 in East Africa. PstS4 was prevalent in Northern Europe on triticale; PstS5 and PstS9 were prevalent in Central Asia; whereas PstS6 was prevalent in epidemics in East Africa. PstS7, PstS8 and PstS10 represented three genetic lineages prevalent in Europe. Races from other lineages were in low frequencies. Virulence to Yr9 and Yr27 was common in epidemics in Africa and Asia, while virulence to Yr17 and Yr32 were prevalent in Europe, corresponding to widely deployed resistance genes. The highest diversity was observed in South Asian populations, where frequent recombination has been reported, and no particular race was predominant in this area. The results are discussed in light of the role of invasions in shaping pathogen population across geographical regions. The results emphasized the lack of predictability of emergence of new races with high epidemic potential, which stresses the need for additional investments in population biology and surveillance activities of pathogens on global food crops, and assessments of disease vulnerability of host varieties prior to their deployment at larger scales.
Keywords: Puccinia striiformis; geographical regions; resistance deployment; virulence phenotyping; wheat.
Figures
References
-
- Ali S., Gladieux P., Leconte M., Gautier A., Justesen A. F., Hovmoller M. S., et al. . (2014a). Origin, migration routes and worldwide population genetic structure of the wheat yellow rust pathogen Puccinia striiformis f.sp. tritici. PLoS Pathogens 10:e1003903. 10.1371/journal.ppat.1003903 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ali S., Gladieux P., Rahman H., Saqib M. S., Fiaz M., Ahmed H., et al. . (2014b). Inferring the contribution of sexual reproduction, migration and off-season survival to the temporal maintenance of microbial populations: a case study on the wheat fungal pathogen Puccinia striiformis f.sp. tritici. Mol. Ecol. 23, 603–617. 10.1111/mec.12629 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ali S., Leconte M., Rahman H., Saqib M. S., Gladieux P., Enjalbert J., et al. (2014c). A high virulence and pathotype diversity of Puccinia striiformis f.sp. tritici at its centre of diversity, the Himalayan region of Pakistan. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 140, 275–290. 10.1007/s10658-014-0461-2 - DOI
-
- Ali S., Shah S. J. A., Khalil I. H., Rahman H., Maqbool K., Ullah W. (2009). Partial resistance to yellow rust in introduced winter wheat germplasm at the north of Pakistan. Aust. J. Crop Sci. 3, 37–43.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources