Photosynthetic Properties and Potentials for Improvement of Photosynthesis in Pale Green Leaf Rice under High Light Conditions
- PMID: 28676818
- PMCID: PMC5476740
- DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2017.01082
Photosynthetic Properties and Potentials for Improvement of Photosynthesis in Pale Green Leaf Rice under High Light Conditions
Abstract
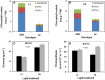
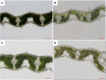
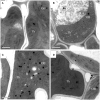
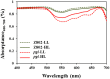
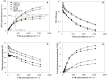
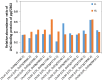
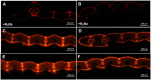
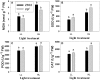
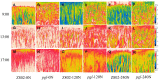
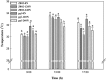
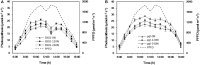
Light is the driving force of plant growth, providing the energy required for photosynthesis. However, photosynthesis is also vulnerable to light-induced damage caused by the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS). Plants have therefore evolved various protective mechanisms such as non-photochemical quenching (NPQ) to dissipate excessively absorbed solar energy as heat; however, photoinhibition and NPQ represent a significant loss in solar energy and photosynthetic efficiency, which lowers the yield potential in crops. To estimate light capture and light energy conversion in rice, a genotype with pale green leaves (pgl) and a normally pigmented control (Z802) were subjected to high (HL) and low light (LL). Chlorophyll content, light absorption, chloroplast micrographs, abundance of light-harvesting complex (LHC) binding proteins, electron transport rates (ETR), photochemical and non-photochemical quenching, and generation of ROS were subsequently examined. Pgl had a smaller size of light-harvesting chlorophyll antenna and absorbed less photons than Z802. NPQ and the generation of ROS were also low, while photosystem II efficiency and ETR were high, resulting in improved photosynthesis and less photoinhibition in pgl than Z802. Chlorophyll synthesis and solar conversion efficiency were higher in pgl under HL compared to LL treatment, while Z802 showed an opposite trend due to the high level of photoinhibition under HL. In Z802, excessive absorption of solar energy not only increased the generation of ROS and NPQ, but also exacerbated the effects of increases in temperature, causing midday depression in photosynthesis. These results suggest that photosynthesis and yield potential in rice could be enhanced by truncated light-harvesting chlorophyll antenna size.
Keywords: chlorophyll; electron transport rate; light-harvesting chlorophyll antenna; non-photochemical quenching; photosynthesis; reactive oxygen species.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Effects of reduced chlorophyll content on photosystem functions and photosynthetic electron transport rate in rice leaves.J Plant Physiol. 2022 May;272:153669. doi: 10.1016/j.jplph.2022.153669. Epub 2022 Mar 23. J Plant Physiol. 2022. PMID: 35344760
-
Harnessing the Role of Foliar Applied Salicylic Acid in Decreasing Chlorophyll Content to Reassess Photosystem II Photoprotection in Crop Plants.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jun 24;23(13):7038. doi: 10.3390/ijms23137038. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35806045 Free PMC article.
-
The knockdown of chloroplastic ascorbate peroxidases reveals its regulatory role in the photosynthesis and protection under photo-oxidative stress in rice.Plant Sci. 2014 Jan;214:74-87. doi: 10.1016/j.plantsci.2013.10.001. Epub 2013 Oct 8. Plant Sci. 2014. PMID: 24268165
-
Biodiversity of NPQ.J Plant Physiol. 2015 Jan 1;172:13-32. doi: 10.1016/j.jplph.2014.03.004. Epub 2014 Mar 25. J Plant Physiol. 2015. PMID: 24854581 Review.
-
LHC-like Proteins: The Guardians of Photosynthesis.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jan 28;24(3):2503. doi: 10.3390/ijms24032503. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36768826 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Seasonal Changes in the Biochemical Constituents of Green Seaweed Chaetomorpha antennina from Covelong, India.Biomolecules. 2022 Oct 13;12(10):1475. doi: 10.3390/biom12101475. Biomolecules. 2022. PMID: 36291683 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluating Photosynthetic Light Response Models for Leaf Photosynthetic Traits in Paddy Rice (Oryza sativa L.) Under Field Conditions.Plants (Basel). 2024 Dec 25;14(1):23. doi: 10.3390/plants14010023. Plants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39795284 Free PMC article.
-
Growth conditions trigger genotype-specific metabolic responses that affect the nutritional quality of kale cultivars.J Exp Bot. 2025 Mar 13;76(5):1427-1445. doi: 10.1093/jxb/erae169. J Exp Bot. 2025. PMID: 38630600 Free PMC article.
-
Mutation in maize chloroplastic polypeptide chain release factor (ZmcpRF1) affects chloroplast development and leaf color.Planta. 2025 Jul 26;262(3):63. doi: 10.1007/s00425-025-04778-y. Planta. 2025. PMID: 40715907
-
Differentially expressed genes related to plant height and yield in two alfalfa cultivars based on RNA-seq.PeerJ. 2022 Oct 10;10:e14096. doi: 10.7717/peerj.14096. eCollection 2022. PeerJ. 2022. PMID: 36248707 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aebi H. (1983). Catalase, in Methods of Enzymatic Analysis, ed Bergmeyer H. U. (New York, NY: Academic Press; ), 273–288.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

