CD40L and Its Receptors in Atherothrombosis-An Update
- PMID: 28676852
- PMCID: PMC5477003
- DOI: 10.3389/fcvm.2017.00040
CD40L and Its Receptors in Atherothrombosis-An Update
Abstract
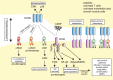
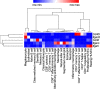
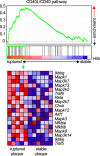
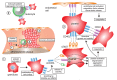
CD40L (CD154), a member of the tumor necrosis factor superfamily, is a co-stimulatory molecule that was first discovered on activated T cells. Beyond its fundamental role in adaptive immunity-ligation of CD40L to its receptor CD40 is a prerequisite for B cell activation and antibody production-evidence from more than two decades has expanded our understanding of CD40L as a powerful modulator of inflammatory pathways. Although inhibition of CD40L with neutralizing antibodies has induced life-threatening side effects in clinical trials, the discovery of cell-specific effects and novel receptors with distinct functional consequences has opened a new path for therapies that specifically target detrimental properties of CD40L. Here, we carefully evaluate the signaling network of CD40L by gene enrichment analysis and its cell-specific expression, and thoroughly discuss its role in cardiovascular pathologies with a specific emphasis on atherosclerotic and thrombotic disease.
Keywords: CD40 signaling; CD40L; Mac-1; atherosclerosis; cardiovascular diseases; inflammation; thrombosis.
Figures
References
-
- Lozano R, Naghavi M, Foreman K, Lim S, Shibuya K, Aboyans V, et al. Global and regional mortality from 235 causes of death for 20 age groups in 1990 and 2010: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010. Lancet (2012) 380(9859):2095–128. 10.1016/S0140-6736(12)61728-0 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

