Methodology, outcome, safety and in vivo accuracy in traditional frame-based stereoelectroencephalography
- PMID: 28676892
- PMCID: PMC5557874
- DOI: 10.1007/s00701-017-3242-9
Methodology, outcome, safety and in vivo accuracy in traditional frame-based stereoelectroencephalography
Abstract
Background: Stereoelectroencephalography (SEEG) is an established diagnostic technique for the localization of the epileptogenic zone in drug-resistant epilepsy. In vivo accuracy of SEEG electrode positioning is of paramount importance since higher accuracy may lead to more precise resective surgery, better seizure outcome and reduction of complications.
Objective: To describe experiences with the SEEG technique in our comprehensive epilepsy center, to illustrate surgical methodology, to evaluate in vivo application accuracy and to consider the diagnostic yield of SEEG implantations.
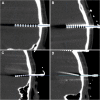
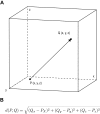
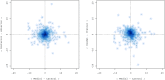
Methods: All patients who underwent SEEG implantations between September 2008 and April 2016 were analyzed. Planned electrode trajectories were compared with post-implantation trajectories after fusion of pre- and postoperative imaging. Quantitative analysis of deviation using Euclidean distance and directional errors was performed. Explanatory variables for electrode accuracy were analyzed using linear regression modeling. The surgical methodology, procedure-related complications and diagnostic yield were reported.
Results: Seventy-six implantations were performed in 71 patients, and a total of 902 electrodes were implanted. Median entry and target point deviations were 1.54 mm and 2.93 mm. Several factors that predicted entry and target point accuracy were identified. The rate of major complications was 2.6%. SEEG led to surgical therapy of various modalities in 53 patients (69.7%).
Conclusions: This study demonstrated that entry and target point localization errors can be predicted by linear regression models, which can aid in identification of high-risk electrode trajectories and further enhancement of accuracy. SEEG is a reliable technique, as demonstrated by the high accuracy of conventional frame-based implantation methodology and the good diagnostic yield.
Keywords: Complications; Epilepsy surgery; In vivo accuracy; Stereoelectroencephalography; Stereotaxy.
Conflict of interest statement
Funding
No funding was received for this research.
Conflict of interest
All authors certify that they have no affiliations with or involvement in any organization or entity with any financial interest (such as honoraria; educational grants; participation in speakers’ bureaus; membership, employment, consultancies, stock ownership, or other equity interest; and expert testimony or patent-licensing arrangements), or non-financial interest (such as personal or professional relationships, affiliations, knowledge or beliefs) in the subject matter or materials discussed in this manuscript.
Ethical approval
For this type of study formal consent is not required.
Informed patient consent
The patients have consented to submission of this Original Article to the journal.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Frameless robot-assisted stereoelectroencephalography for refractory epilepsy in pediatric patients: accuracy, usefulness, and technical issues.Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2018 Dec;160(12):2489-2500. doi: 10.1007/s00701-018-3720-8. Epub 2018 Nov 9. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2018. PMID: 30413938
-
The stereotactic approach for mapping epileptic networks: a prospective study of 200 patients.J Neurosurg. 2014 Nov;121(5):1239-46. doi: 10.3171/2014.7.JNS132306. Epub 2014 Aug 22. J Neurosurg. 2014. PMID: 25148007
-
Indications, technique, and safety profile of insular stereoelectroencephalography electrode implantation in medically intractable epilepsy.J Neurosurg. 2018 Apr;128(4):1147-1157. doi: 10.3171/2017.1.JNS161070. Epub 2017 Jun 16. J Neurosurg. 2018. PMID: 28621621
-
Stereoelectroencephalography: Indication and Efficacy.Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo). 2017 Aug 15;57(8):375-385. doi: 10.2176/nmc.ra.2017-0008. Epub 2017 Jun 20. Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo). 2017. PMID: 28637943 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Invasive EEG-electrodes in presurgical evaluation of epilepsies: Systematic analysis of implantation-, video-EEG-monitoring- and explantation-related complications, and review of literature.Epilepsy Behav. 2019 Feb;91:30-37. doi: 10.1016/j.yebeh.2018.05.012. Epub 2018 Jun 13. Epilepsy Behav. 2019. PMID: 29907526
Cited by
-
Robot-assisted stereoencephalography vs subdural electrodes in the evaluation of temporal lobe epilepsy.Epilepsia Open. 2023 Sep;8(3):888-897. doi: 10.1002/epi4.12756. Epub 2023 May 14. Epilepsia Open. 2023. PMID: 37149851 Free PMC article.
-
Stereoelectroencephalography in the very young: Case report.Epilepsy Behav Rep. 2022 May 18;19:100552. doi: 10.1016/j.ebr.2022.100552. eCollection 2022. Epilepsy Behav Rep. 2022. PMID: 35664664 Free PMC article.
-
VarioGuide® frameless neuronavigation-guided stereoelectroencephalography in adult epilepsy patients: technique, accuracy and clinical experience.Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2021 May;163(5):1355-1364. doi: 10.1007/s00701-021-04755-w. Epub 2021 Feb 13. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2021. PMID: 33580853 Free PMC article.
-
Frame-based versus robot-assisted stereo-electro-encephalography for drug-resistant epilepsy.Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2024 Feb 16;166(1):85. doi: 10.1007/s00701-024-05983-6. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2024. PMID: 38361129
-
Dataset of Speech Production in intracranial.Electroencephalography.Sci Data. 2022 Jul 22;9(1):434. doi: 10.1038/s41597-022-01542-9. Sci Data. 2022. PMID: 35869138 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bancaud J, Angelergues R, Bernouilli C, et al. Functional stereotaxic exploration (stereo-electroencephalography) in epilepsies. Rev Neurol (Paris) 1969;120(6):448. - PubMed
-
- Bancaud J, Talairach J (1973) Methodology of stereo EEG exploration and surgical intervention in epilepsy. Rev Otoneuroophtalmol 45(4):315–328 - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

