Carboxylesterases in lipid metabolism: from mouse to human
- PMID: 28677105
- PMCID: PMC5818367
- DOI: 10.1007/s13238-017-0437-z
Carboxylesterases in lipid metabolism: from mouse to human
Abstract
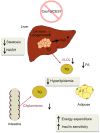
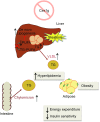
Mammalian carboxylesterases hydrolyze a wide range of xenobiotic and endogenous compounds, including lipid esters. Physiological functions of carboxylesterases in lipid metabolism and energy homeostasis in vivo have been demonstrated by genetic manipulations and chemical inhibition in mice, and in vitro through (over)expression, knockdown of expression, and chemical inhibition in a variety of cells. Recent research advances have revealed the relevance of carboxylesterases to metabolic diseases such as obesity and fatty liver disease, suggesting these enzymes might be potential targets for treatment of metabolic disorders. In order to translate pre-clinical studies in cellular and mouse models to humans, differences and similarities of carboxylesterases between mice and human need to be elucidated. This review presents and discusses the research progress in structure and function of mouse and human carboxylesterases, and the role of these enzymes in lipid metabolism and metabolic disorders.
Keywords: adipose; carboxylesterase; intestine; lipase; lipid; lipoprotein; liver.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Human carboxylesterases in term placentae: enzymatic characterization, molecular cloning and evidence for the existence of multiple forms.Placenta. 1999 Sep;20(7):599-607. doi: 10.1053/plac.1999.0407. Placenta. 1999. PMID: 10452915
-
Structure, function and regulation of carboxylesterases.Chem Biol Interact. 2006 Sep 25;162(3):195-211. doi: 10.1016/j.cbi.2006.07.001. Epub 2006 Jul 6. Chem Biol Interact. 2006. PMID: 16919614 Review.
-
Substrate specificity and kinetic properties of enzymes belonging to the hormone-sensitive lipase family: comparison with non-lipolytic and lipolytic carboxylesterases.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2005 Dec 30;1738(1-3):29-36. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2005.11.003. Epub 2005 Nov 17. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2005. PMID: 16325466
-
Carboxylesterase Inhibitors: An Update.Curr Med Chem. 2018;25(14):1627-1649. doi: 10.2174/0929867325666171204155558. Curr Med Chem. 2018. PMID: 29210644 Review.
-
Recent advances of structure, function, and engineering of carboxylesterases for the pharmaceutical industry: A minireview.Int J Biol Macromol. 2025 May;307(Pt 3):142206. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2025.142206. Epub 2025 Mar 17. Int J Biol Macromol. 2025. PMID: 40107535 Review.
Cited by
-
Impaired cholesterol efflux in retinal pigment epithelium of individuals with juvenile macular degeneration.Am J Hum Genet. 2021 May 6;108(5):903-918. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2021.04.006. Epub 2021 Apr 27. Am J Hum Genet. 2021. PMID: 33909993 Free PMC article.
-
Control of Protein and Energy Metabolism in the Pituitary Gland in Response to Three-Week Running Training in Adult Male Mice.Cells. 2021 Mar 26;10(4):736. doi: 10.3390/cells10040736. Cells. 2021. PMID: 33810540 Free PMC article.
-
Sex-Dependent Responses to Maternal Exposure to PM2.5 in the Offspring.Antioxidants (Basel). 2022 Nov 15;11(11):2255. doi: 10.3390/antiox11112255. Antioxidants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36421441 Free PMC article.
-
Overcoming insecticide resistance through computational inhibitor design.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019 Oct 15;116(42):21012-21021. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1909130116. Epub 2019 Oct 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019. PMID: 31575743 Free PMC article.
-
Carboxylesterase 1 family knockout alters drug disposition and lipid metabolism.Acta Pharm Sin B. 2023 Feb;13(2):618-631. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2022.10.017. Epub 2022 Oct 25. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2023. PMID: 36873183 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

