Chiral Nanotubes
- PMID: 28677640
- PMCID: PMC5535233
- DOI: 10.3390/nano7070167
Chiral Nanotubes
Abstract
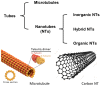
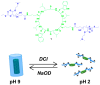
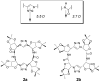
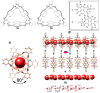
Organic nanotubes, as assembled nanospaces, in which to carry out host-guest chemistry, reversible binding of smaller species for transport, sensing, storage or chemical transformation purposes, are currently attracting substantial interest, both as biological ion channel mimics, or for addressing tailored material properties. Nature's materials and machinery are universally asymmetric, and, for chemical entities, controlled asymmetry comes from chirality. Together with carbon nanotubes, conformationally stable molecular building blocks and macrocycles have been used for the realization of organic nanotubes, by means of their assembly in the third dimension. In both cases, chiral properties have started to be fully exploited to date. In this paper, we review recent exciting developments in the synthesis and assembly of chiral nanotubes, and of their functional properties. This review will include examples of either molecule-based or macrocycle-based systems, and will try and rationalize the supramolecular interactions at play for the three-dimensional (3D) assembly of the nanoscale architectures.
Keywords: anisotropic materials; chirality; nanotubes; supramolecular polymers; three-dimensional (3D) assembly.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
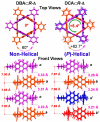
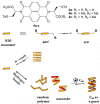
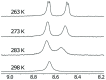
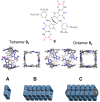
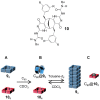
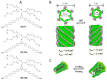

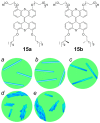

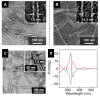
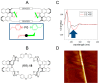
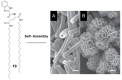
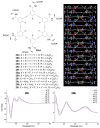
References
-
- Soldano C. Hybrid metal-based carbon nanotubes: Novel platform for multifunctional applications. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2015;69:183–212. doi: 10.1016/j.pmatsci.2014.11.001. - DOI
-
- Ebbesen T.W., Ajayan P.M. Large-scale synthesis of carbon nanotubes. Nature. 1992;358:220–222. doi: 10.1038/358220a0. - DOI
-
- Guo T., Nikolaev P., Thess A., Colbert D.T., Smalley R.E. Catalytic growth of single-walled nanotubes by laser vaporization. Chem. Phys. Lett. 1995;243:49–54. doi: 10.1016/0009-2614(95)00825-O. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

