Cryo-EM structures of tau filaments from Alzheimer's disease
- PMID: 28678775
- PMCID: PMC5552202
- DOI: 10.1038/nature23002
Cryo-EM structures of tau filaments from Alzheimer's disease
Abstract
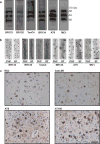
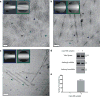
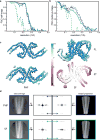
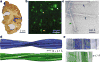
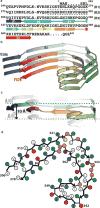
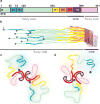
Alzheimer's disease is the most common neurodegenerative disease, and there are no mechanism-based therapies. The disease is defined by the presence of abundant neurofibrillary lesions and neuritic plaques in the cerebral cortex. Neurofibrillary lesions comprise paired helical and straight tau filaments, whereas tau filaments with different morphologies characterize other neurodegenerative diseases. No high-resolution structures of tau filaments are available. Here we present cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM) maps at 3.4-3.5 Å resolution and corresponding atomic models of paired helical and straight filaments from the brain of an individual with Alzheimer's disease. Filament cores are made of two identical protofilaments comprising residues 306-378 of tau protein, which adopt a combined cross-β/β-helix structure and define the seed for tau aggregation. Paired helical and straight filaments differ in their inter-protofilament packing, showing that they are ultrastructural polymorphs. These findings demonstrate that cryo-EM allows atomic characterization of amyloid filaments from patient-derived material, and pave the way for investigation of a range of neurodegenerative diseases.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures
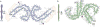
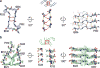
Comment in
-
Neurodegeneration: Taming tangled tau.Nature. 2017 Jul 13;547(7662):170-171. doi: 10.1038/nature23094. Epub 2017 Jul 5. Nature. 2017. PMID: 28678777 Free PMC article.
-
Alzheimer disease: Tau pathology in atomic detail.Nat Rev Neurol. 2017 Sep;13(9):513. doi: 10.1038/nrneurol.2017.107. Epub 2017 Jul 21. Nat Rev Neurol. 2017. PMID: 28731038 No abstract available.
References
-
- Wilcock GK, Esiri MM. Plaques, tangles and dementia. A quantitative study. J Neurol Sci. 1982;56:343–356. - PubMed
-
- Kidd M. Paired helical filaments in electron microscopy of Alzheimer’s disease. Nature. 1963;197:192–193. - PubMed
-
- Terry RD. The fine structure of neurofibrillary tangles in Alzheimer’s disease. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1963;22:629–642. - PubMed
-
- Yagishita S, Itoh Y, Nan W, Amano N. Reappraisal of the fine structure of Alzheimer’s neurofibrillary tangles. Acta Neuropathol. 1981;54:239–246. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

