HMGB3 promotes growth and migration in colorectal cancer by regulating WNT/β-catenin pathway
- PMID: 28678825
- PMCID: PMC5497964
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0179741
HMGB3 promotes growth and migration in colorectal cancer by regulating WNT/β-catenin pathway
Abstract
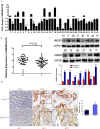
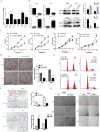
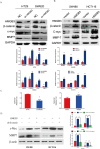
Colorectal cancer (CRC) is the third leading cause of cancer-related deaths and a major health problem. High mobility group box 3 (HMGB3), a member of the high-mobility group box (HMGB) family, was reported to be over-expressed in gastric carcinoma and bladder cancer. However, the function of HMGB3 in CRC remains unclear. Here, we found that HMGB3 was up-regulated in CRC at both mRNA and protein levels. qRT-PCR results showed that high expression of HMGB3 had positive correlation with serosal invasion, lymph metastasis, and tumor-node-metastasis (TNM) stage in CRC patient. Functional experiments showed that HMGB3 can promote CRC cells proliferation and migration in vitro. Moreover, we found HMGB3 can active WNT/β-catenin pathway to increase the expression level of c-Myc and MMP7. These results may be the reason for HMGB3 oncogene role in CRC. In summary, our data indicated that HMGB3 may serve as an oncoprotein and could be used as a potential prognostic marker in CRC.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Herszenyi L, Tulassay Z. Epidemiology of gastrointestinal and liver tumors. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2010; 14: 249–258. - PubMed
-
- Emmons KM, Burns White K, Benz EJ. Development of an integrated approach to cancer disparities: one cancer center's experience. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2007; 16: 2186–2192. doi: 10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-07-0211 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Center MM, Jemal A, Smith RA, Ward E. Worldwide variations in colorectal cancer. CA Cancer J Clin. 2009; 59: 366–378. doi: 10.3322/caac.20038 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bray F, Ren JS, Masuyer E, Ferlay J. Global estimates of cancer prevalence for 27 sites in the adult population in 2008. Int J Cancer. 2013; 132: 1133–1145. doi: 10.1002/ijc.27711 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Calon A, Espinet E, Palomo-Ponce S, Tauriello DV, Iglesias M, Cespedes MV, et al. Dependency of colorectal cancer on a TGF-beta-driven program in stromal cells for metastasis initiation. Cancer Cell. 2012; 22: 571–584. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2012.08.013 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

