Global Longitudinal Strain or Left Ventricular Twist and Torsion? Which Correlates Best with Ejection Fraction?
- PMID: 28678927
- PMCID: PMC5524472
- DOI: 10.5935/abc.20170085
Global Longitudinal Strain or Left Ventricular Twist and Torsion? Which Correlates Best with Ejection Fraction?
Abstract
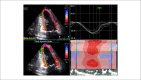
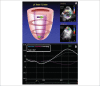
Background: Estimative of left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) is a major indication for echocardiography. Speckle tracking echocardiography (STE) allows analysis of LV contraction mechanics which includes global longitudinal strain (GLS) and twist/torsion, both the most widely used. Direct comparison of correlations between these novel parameters and LVEF has never been done before.
Objective: This study aims to check which one has the highest correlation with LVEF.
Methods: Patients with normal LVEF (> 0,55) and systolic dysfunction (LVEF <0,55) were prospectively enrolled, and underwent echocardiogram with STE analysis. Correlation of variables was performed by linear regression analysis. In addition, correlation among levels of LV systolic impairment was also tested.
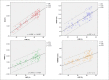
Results: A total of 131 patients were included (mean age, 46 ± 14y; 43%, men). LVEF and GLS showed a strong correlation (r = 0.95; r2 = 0.89; p < 0.001), more evident in groups with LV systolic dysfunction than those with preserved LVEF. Good correlation was also found with global longitudinal strain rate (r = 0.85; r2 = 0.73; p < 0.001). Comparing to GLS, correlation of LVEF and torsional mechanics was weaker: twist (r = 0.78; r2 = 0.60; p < 0.001); torsion (r = 0.75; r2 = 0.56; p < 0.001).
Conclusion: GLS of the left ventricle have highly strong positive correlation with the classical parameter of ejection fraction, especially in cases with LV systolic impairment. Longitudinal strain rate also demonstrated a good correlation. GLS increments analysis of LV systolic function. On the other hand, although being a cornerstone of LV mechanics, twist and torsion have a weaker correlation with LV ejection, comparing to GLS.
Fundamento: A estimativa da fração de ejeção do ventrículo esquerdo (FEVE) é uma das pincipais indicações para a ecocardiografia. Speckle tracking (ST) permite a análise da mecânica de contração do VE que inclui a deformação (strain) longitudinal global (SLG) e o twist / torção, sendo ambos os mais utilizados. A comparação direta de correlações entre esses novos parâmetros e a FEVE nunca foi feita antes.
Objetivo: Verificar qual delas tem a maior correlação com a FEVE.
Métodos: Pacientes com FEVE normal (> 0,55) e disfunção sistólica (FEVE < 0,55) foram prospectivamente inscritos e submetidos a ecocardiograma com análise do ST. A correlação das variáveis foi realizada por análise de regressão linear. Além disso, também foi testada a correlação entre os níveis de comprometimento sistólico do VE.
Resultados: Foram incluídos 131 pacientes (média de idade de 46 ± 14 anos e 43% de homens). A FEVE e SLG apresentaram forte correlação (r = 0,95; r2 = 0,89; p < 0,001), mais evidente em grupos com disfunção sistólica do VE do que naqueles com FEVE preservada. Também foi encontrada boa correlação com a taxa de deformação (strain rate) longitudinal (SRL) global (r = 0,85; r2 = 0,73; p < 0,001). Comparando-a à SLG, a correlação entre FEVE e mecânica de torção foi mais fraca: twist (r = 0,78; r2 = 0,60; p < 0,001); Torção (r = 0,75, r2 = 0,56, p < 0,001).
Conclusão: A SLG do ventrículo esquerdo apresenta alta correlação positiva com o parâmetro clássico de fração de ejeção, principalmente nos casos de comprometimento sistólico do VE. O SRL também demonstrou uma boa correlação. A SLG incrementa a análise da função sistólica do VE. Por outro lado, apesar de ser a pedra angular da mecânica do VE, o twist e a torção têm uma correlação mais fraca com a ejeção do VE, quando comparados ao SLG.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Assessment of left ventricular twist mechanics by two-dimensional strain in severe aortic stenosis with preserved ejection fraction].Ann Cardiol Angeiol (Paris). 2011 Nov;60(5):259-66. doi: 10.1016/j.ancard.2011.08.002. Epub 2011 Aug 26. Ann Cardiol Angeiol (Paris). 2011. PMID: 21903195 French.
-
Prevalence of left ventricular systolic dysfunction in pre-dialysis and dialysis patients with preserved left ventricular ejection fraction.Eur J Heart Fail. 2018 Mar;20(3):560-568. doi: 10.1002/ejhf.1077. Epub 2017 Nov 21. Eur J Heart Fail. 2018. PMID: 29164753
-
Left ventricular systolic function assessment in secondary mitral regurgitation: left ventricular ejection fraction vs. speckle tracking global longitudinal strain.Eur Heart J. 2016 Mar 7;37(10):811-6. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehv680. Epub 2015 Dec 18. Eur Heart J. 2016. PMID: 26685140
-
Left ventricular systolic function evaluated by strain echocardiography and relationship with mortality in patients with severe sepsis or septic shock: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Crit Care. 2018 Aug 4;22(1):183. doi: 10.1186/s13054-018-2113-y. Crit Care. 2018. PMID: 30075792 Free PMC article.
-
Assessment of Left Ventricular Function by Echocardiography: The Case for Routinely Adding Global Longitudinal Strain to Ejection Fraction.JACC Cardiovasc Imaging. 2018 Feb;11(2 Pt 1):260-274. doi: 10.1016/j.jcmg.2017.11.017. JACC Cardiovasc Imaging. 2018. PMID: 29413646 Review.
Cited by
-
Early detection of reduced left ventricular systolic function by 2D speckle tracking echocardiography in patients with primary mitral regurgitation in a Vietnamese cohort.Glob Cardiol Sci Pract. 2023 Sep 30;2023(4):e202326. doi: 10.21542/gcsp.2023.26. eCollection 2023 Sep 30. Glob Cardiol Sci Pract. 2023. PMID: 38623555 Free PMC article.
-
Deformation imaging to assess global and regional effects of cardiac regenerative therapy in ischaemic heart disease: A systematic review.J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2019 Oct;13(10):1872-1882. doi: 10.1002/term.2937. Epub 2019 Sep 1. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2019. PMID: 31314949 Free PMC article.
-
Cardiac Involvement in LAMA2-Related Muscular Dystrophy and SELENON-Related Congenital Myopathy: A Case Series.J Neuromuscul Dis. 2024;11(5):919-934. doi: 10.3233/JND-230190. J Neuromuscul Dis. 2024. PMID: 39177608 Free PMC article.
-
3D echocardiography derived reference values and determinants of left ventricular twist and torsion from the population-based STAAB cohort study.Sci Rep. 2025 Feb 6;15(1):4524. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-81662-x. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 39915496 Free PMC article.
-
Assessment of left ventricular twist by 3D ballistocardiography and seismocardiography compared with 2D STI echocardiography in a context of enhanced inotropism in healthy subjects.Sci Rep. 2021 Jan 12;11(1):683. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-79933-4. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 33436841 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Langeland S, D'Hooge J, Wouters PF, Leather HA, Claus P, Bijnens B, et al. Experimental validation of a new ultrasound method for the simultaneous assessment of radial and longitudinal myocardial deformation independent of insonation angle. Circulation. 2005;112(14):2157–2162. - PubMed
-
- Helle-Valle T, Crosby J, Edvardsen T, Lyseggen E, Amundsen BH, Smith HJ, et al. New noninvasive method for assessment of left ventricular rotation - Speckle tracking echocardiography. Circulation. 2005;112(20):3149–3156. - PubMed
-
- Amundsen BH, Helle-Valle T, Edvardsen T, Torp H, Crosby J, Lyseggen E, et al. Noninvasive myocardial strain measurement by speckle tracking echocardiography - Validation against sonomicrometry and tagged magnetic resonance imaging. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2006;47(4):789–793. - PubMed
-
- Edvardsen T, Helle-Valle T, Smiseth OA. Systolic dysfunction in heart failure with normal ejection fraction: Speckle-tracking echocardiography. Prog Cardiovasc Dis. 2006;49(3):207–214. - PubMed
-
- Notomi Y, Lysyansky P, Setser RM, Shiota T, Popovic ZB, Martin-Miklovic MG, et al. Measurement of ventricular torsion by two-dimensional ultrasound speckle tracking imaging. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2005;45(12):2034–2041. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

