Effects of aerobic exercise on lipids and lipoproteins
- PMID: 28679436
- PMCID: PMC5498979
- DOI: 10.1186/s12944-017-0515-5
Effects of aerobic exercise on lipids and lipoproteins
Abstract
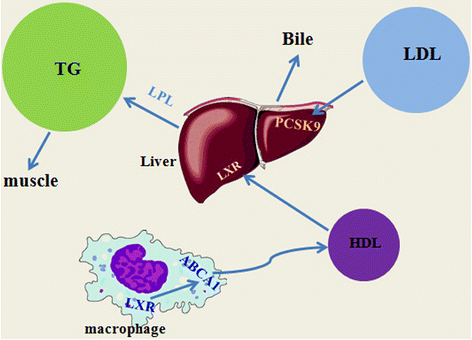
Dyslipidemia is the risk of cardiovascular disease, and their relationship is clear. Lowering serum cholesterol can reduce the risk of coronary heart disease. At present, the main treatment is taking medicine, however, drug treatment has its limitations. Exercise not only has a positive effect on individuals with dyslipidemia, but can also help improve lipids profile. This review is intending to provide information on the effects of exercise training on both tranditional lipids, for example, low-density lipoprotein cholesterol, high-density lipoprotein cholesterol, triglycerides and new lipids and lipoproteins such as non-high-density lipoprotein cholesterol, and postprandial lipoprotein. The mechanisms of aerobic exercise on lipids and lipoproteins are also briefly described.
Keywords: Aerobic exercise; Coronary heart disease; Dyslipidemia; Lipoprotein.
Figures
References
-
- Goff DC, Jr, Lloyd-Jones DM, Bennett G, et al. 2013 ACC/AHA guideline on the assessment of cardiovascular risk: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines. Circulation. 2014;129(suppl 2):S49–S73. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.0000437741.48606.98. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Nordestgaard BG, Wootton R, Lewis B. Selective retention of VLDL, ODL, and LDL in the arterial intima of genetically hyperlipidemic rabbits in vivo. Molecular size as a determinant of fractional loss from the intima-inner media. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 1995;15:534–542. doi: 10.1161/01.ATV.15.4.534. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

